How To Install Snipe-IT on Fedora 42

Managing IT assets efficiently has become crucial for organizations of all sizes. Snipe-IT stands out as the leading open-source asset management solution, offering comprehensive tracking capabilities for hardware, software, and digital resources. This powerful Laravel-based application provides robust features including asset lifecycle management, automated depreciation calculations, and detailed reporting functionality.
Fedora 42, with its cutting-edge package management and enterprise-grade stability, serves as an excellent platform for hosting Snipe-IT deployments. The combination delivers exceptional performance while maintaining security standards required for production environments. This comprehensive installation guide walks you through every step of deploying Snipe-IT on Fedora 42, from initial system preparation to final configuration optimization.
Whether you’re a system administrator implementing your first asset management system or an experienced professional migrating to a more robust platform, this tutorial provides detailed instructions, troubleshooting solutions, and best practices. The complete installation process typically takes 45-60 minutes, depending on system specifications and network connectivity.
Understanding Snipe-IT Architecture
Core Features and Benefits
Snipe-IT revolutionizes asset management through its comprehensive feature set built on the Laravel PHP framework. The application excels at tracking physical assets like laptops, servers, and mobile devices while simultaneously managing software licenses and digital resources. Its RESTful API enables seamless integration with existing business systems, making it ideal for organizations requiring automated workflows.
The platform supports unlimited users with granular role-based permissions, allowing administrators to control access levels precisely. Advanced reporting capabilities provide insights into asset utilization, maintenance schedules, and financial depreciation calculations. Multi-company support enables managed service providers to serve multiple clients from a single installation.
System Architecture Overview
The application operates on a traditional LAMP stack architecture (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP), ensuring compatibility with standard web hosting environments. Snipe-IT’s database-driven design stores all asset information, user data, and configuration settings in MariaDB or MySQL databases. The web-based interface provides responsive design elements, making it accessible from desktop computers, tablets, and mobile devices.
File storage utilizes both database records and filesystem directories for uploaded images, documentation, and asset attachments. This hybrid approach optimizes performance while maintaining data integrity and backup simplicity.
Prerequisites and System Requirements
Hardware Requirements
Production Snipe-IT deployments require adequate system resources to handle concurrent users and extensive asset databases. Minimum specifications include 2GB RAM, dual-core processor, and 20GB available disk space. However, organizations managing thousands of assets should consider 4GB RAM, quad-core processor, and 50GB+ storage capacity.
Network connectivity requirements include reliable internet access for software updates, email notifications, and potential API integrations. Consider implementing redundant network connections for mission-critical deployments. Storage performance significantly impacts database operations, making SSD storage highly recommended for production environments.
Software Dependencies
Fedora 42 provides modern package versions perfectly suited for Snipe-IT deployment. PHP version compatibility spans from 7.4 through 8.1.2, with PHP 8.1 offering optimal performance and security features. Apache web server 2.4+ delivers the necessary mod_rewrite and virtual host capabilities required for proper URL routing.
MariaDB 10.3+ or MySQL 5.7+ provides the database foundation, with MariaDB recommended for superior performance and open-source licensing. Git version control enables easy updates and version management, while Composer handles PHP dependency resolution and package management.
Essential PHP extensions include:
- php-mbstring for multibyte string handling
- php-xml for XML processing capabilities
- php-gd for image manipulation functions
- php-curl for HTTP client operations
- php-zip for archive handling
- php-intl for internationalization support
Pre-Installation System Preparation
System Updates and Security Configuration
Begin by updating all Fedora 42 packages to ensure system security and compatibility. Execute the following commands to refresh package repositories and install available updates:
sudo dnf update -y
sudo dnf upgrade -yConfigure firewall rules to allow HTTP and HTTPS traffic while maintaining system security. Enable the necessary ports using firewall-cmd:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadSELinux considerations require temporary adjustments during installation. While maintaining security is crucial, some configuration steps may require permissive mode:
sudo setenforce 0
sudo sed -i 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=permissive/' /etc/selinux/configCreate a dedicated user account with sudo privileges for enhanced security practices. Avoid performing installation tasks as the root user:
sudo adduser snipeit-admin
sudo usermod -aG wheel snipeit-adminInstalling Core Components
Install Apache web server and configure it for automatic startup:
sudo dnf install httpd -y
sudo systemctl enable httpd
sudo systemctl start httpdDeploy MariaDB server with security hardening:
sudo dnf install mariadb-server mariadb -y
sudo systemctl enable mariadb
sudo systemctl start mariadb
sudo mysql_secure_installationInstall PHP 8.3 with all required extensions for optimal Snipe-IT performance:
sudo dnf install php php-cli php-fpm php-mysql php-json php-opcache php-xml php-mbstring php-gd php-curl php-zip php-intl php-bcmath php-tokenizer php-fileinfo -yDeploy Composer for PHP dependency management:
curl -sS https://getcomposer.org/installer | php
sudo mv composer.phar /usr/local/bin/composer
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/composerInstall Git for repository management and updates:
sudo dnf install git -yVerify service status and ensure proper startup configuration:
sudo systemctl status httpd mariadb php-fpmDatabase Configuration
MariaDB Security and Database Creation
Secure the MariaDB installation by running the security script and following the prompts:
sudo mysql_secure_installationDuring the security configuration, set a strong root password, remove anonymous users, disable remote root login, and remove test databases. These steps significantly enhance database security.
Access MariaDB as the root user and create a dedicated database for Snipe-IT:
sudo mysql -u root -pExecute the following SQL commands within the MariaDB prompt:
CREATE DATABASE snipeit_db CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
CREATE USER 'snipeit_user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'StrongPassword123!';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON snipeit_db.* TO 'snipeit_user'@'localhost';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
EXIT;Password security practices dictate using complex passwords combining uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Store database credentials securely and avoid reusing passwords across different services.
Database Optimization Settings
Configure MariaDB for optimal Snipe-IT performance by editing the configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnfAdd or modify the following settings under the [mysqld] section:
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 256M
innodb_log_file_size = 64M
query_cache_type = 1
query_cache_size = 32M
max_connections = 200Restart MariaDB to apply the new configuration:
sudo systemctl restart mariadbDownloading and Installing Snipe-IT
Repository Clone and Directory Setup
Create the web directory structure with appropriate permissions:
cd /var/www/
sudo git clone https://github.com/snipe/snipe-it.git
sudo chown -R apache:apache snipe-it/
sudo chmod -R 755 snipe-it/Navigate to the Snipe-IT directory and examine the file structure:
cd snipe-it/
ls -laThe repository contains essential directories including app/ for application logic, config/ for configuration files, storage/ for uploads and logs, and public/ for web-accessible files.
Alternative download methods include downloading ZIP archives directly from GitHub. This approach suits environments with limited Git access:
wget https://github.com/snipe/snipe-it/archive/master.zip
unzip master.zip
mv snipe-it-master snipe-itComposer Dependencies Installation
Install production dependencies using Composer with optimized settings:
cd /var/www/snipe-it/
composer install --no-dev --prefer-sourceThe --no-dev flag excludes development packages, reducing installation size and improving security. The --prefer-source option ensures compatibility with various hosting environments by downloading source code rather than distribution packages.
Troubleshooting Composer issues often involves memory limitations or network timeouts. Increase PHP memory limits temporarily:
php -d memory_limit=512M /usr/local/bin/composer install --no-dev --prefer-sourceMonitor the installation process for dependency conflicts or missing extensions. Address any reported issues by installing additional PHP modules or adjusting server configuration.
Application Configuration
Environment File Configuration
Copy the example environment file and customize it for your installation:
cp .env.example .env
nano .envConfigure database connection settings matching your MariaDB setup:
DB_CONNECTION=mysql
DB_HOST=127.0.0.1
DB_PORT=3306
DB_DATABASE=snipeit_db
DB_USERNAME=snipeit_user
DB_PASSWORD=StrongPassword123!Set the application URL to match your domain configuration:
APP_URL=http://your-domain.com
APP_TIMEZONE='America/New_York'
APP_LOCALE=enMail server configuration enables notification functionality:
MAIL_DRIVER=smtp
MAIL_HOST=smtp.gmail.com
MAIL_PORT=587
MAIL_ENCRYPTION=tls
MAIL_USERNAME=your-email@gmail.com
MAIL_PASSWORD=your-app-passwordGenerate the application encryption key using Laravel Artisan:
php artisan key:generateFile Permissions and Security Hardening
Set correct ownership and permissions for web server access:
sudo chown -R apache:apache /var/www/snipe-it/
sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www/snipe-it/
sudo chmod -R 775 /var/www/snipe-it/storage/
sudo chmod -R 775 /var/www/snipe-it/bootstrap/cache/Security considerations require protecting sensitive configuration files from unauthorized access:
sudo chmod 600 /var/www/snipe-it/.env
sudo chattr +i /var/www/snipe-it/.envThe chattr +i command makes the environment file immutable, preventing accidental modifications or unauthorized changes.
Web Server Configuration
Apache Virtual Host Setup
Create a comprehensive virtual host configuration for Snipe-IT:
sudo nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/snipe-it.confAdd the following virtual host configuration:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName your-domain.com
ServerAlias www.your-domain.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/snipe-it/public
<Directory /var/www/snipe-it/public>
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/snipe-it_error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/snipe-it_access.log combined
</VirtualHost>AllowOverride and mod_rewrite configuration enables Laravel’s URL routing. Enable the rewrite module:
sudo dnf install httpd-devel -y
echo "LoadModule rewrite_module modules/mod_rewrite.so" | sudo tee -a /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.confTest virtual host syntax before restarting Apache:
sudo httpd -t
sudo systemctl restart httpdServer Optimization and Module Configuration
Enable essential Apache modules for enhanced performance:
sudo nano /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.confEnsure the following modules are loaded:
LoadModule rewrite_module modules/mod_rewrite.so
LoadModule deflate_module modules/mod_deflate.so
LoadModule expires_module modules/mod_expires.so
LoadModule headers_module modules/mod_headers.soPerformance tuning involves configuring compression and caching:
<IfModule mod_deflate.c>
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/plain
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/html
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/xml
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/css
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/xml
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/xhtml+xml
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/rss+xml
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/javascript
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/x-javascript
</IfModule>Database Migration and Initial Setup
Running Laravel Artisan Commands
Execute database migrations to create the necessary table structure:
cd /var/www/snipe-it/
php artisan migrate --forceThe --force flag bypasses confirmation prompts, suitable for automated deployments. Monitor the migration process for any errors or warnings indicating database connectivity issues.
Generate and cache configuration files for improved performance:
php artisan config:cache
php artisan route:cache
php artisan view:cacheApplication key verification ensures proper encryption functionality:
php artisan key:generate --showAdministrator Account Creation
Create the first administrator account through the web interface or command line. Access the application through your configured domain and complete the setup wizard. Provide administrator credentials, company information, and initial configuration preferences.
Strong password practices should include minimum 12 characters with complexity requirements. Enable two-factor authentication when available for enhanced security.
Test login functionality and verify dashboard accessibility. Confirm email configuration by triggering a test notification.
Testing and Verification
Functionality Testing
Access the web interface using your configured domain. Verify the login page loads correctly without errors. Test database connectivity by creating a test asset category and confirming data persistence.
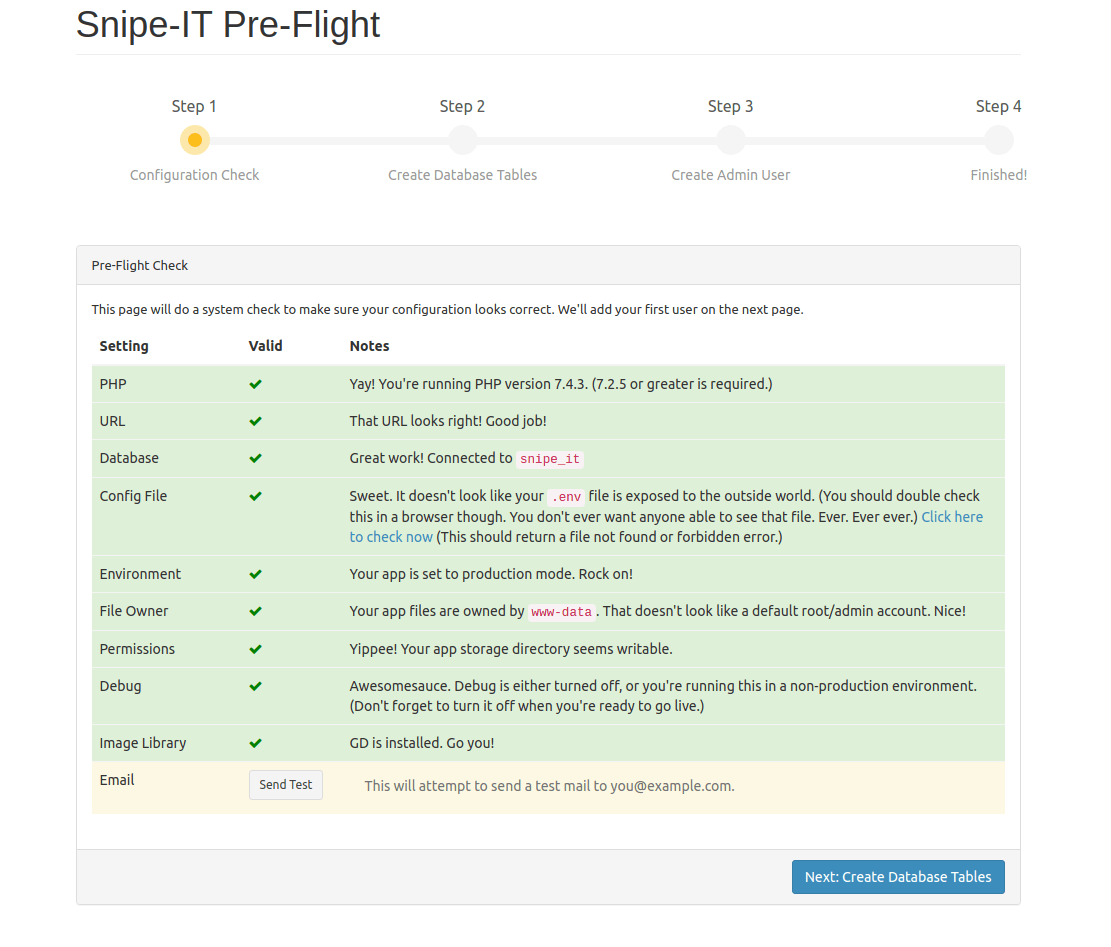
File upload functionality testing involves uploading asset images and documentation. Navigate to Settings > File Uploads and test various file formats to ensure proper handling.
Verify email configuration by triggering password reset notifications or user invitation emails. Check server logs for any SMTP connection errors or delivery failures.
Performance Validation and Monitoring
Assess page load times using browser developer tools or external monitoring services. Target response times under 2 seconds for optimal user experience. Monitor database query performance through Laravel’s built-in debugging tools.
Memory usage monitoring helps identify resource bottlenecks:
ps aux | grep apache
free -h
top -p $(pgrep httpd | tr '\n' ',' | sed 's/,$//')Test concurrent user access by opening multiple browser sessions and performing simultaneous operations. Monitor server responsiveness and identify any performance degradation.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Database Connection Problems
Credential verification in the .env file represents the most common connection issue. Double-check username, password, database name, and host settings:
mysql -u snipeit_user -p snipeit_dbSuccessful connection confirms database credentials. If connection fails, verify user permissions and password accuracy.
MariaDB service status checking resolves service-related connectivity issues:
sudo systemctl status mariadb
sudo journalctl -u mariadb -fWeb Server Configuration Issues
Apache error log analysis provides detailed troubleshooting information:
sudo tail -f /var/log/httpd/error_log
sudo tail -f /var/log/httpd/snipe-it_error.logCommon errors include mod_rewrite disabled, incorrect document root, or permission issues. Virtual host configuration problems often manifest as 404 errors or incorrect page loading.
Verify mod_rewrite functionality:
apache2ctl -M | grep rewritePermission and Security Errors
File and directory ownership correction resolves access denied errors:
sudo chown -R apache:apache /var/www/snipe-it/
find /var/www/snipe-it/ -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;
find /var/www/snipe-it/ -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;
chmod -R 775 /var/www/snipe-it/storage/SELinux policy conflicts require specific context configuration:
sudo setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect on
sudo restorecon -R /var/www/snipe-it/Storage directory write permissions must allow Apache user access:
sudo chmod -R 775 /var/www/snipe-it/storage/
sudo chmod -R 775 /var/www/snipe-it/bootstrap/cache/Performance Optimization and Best Practices
Caching Strategies Implementation
PHP OPcache configuration significantly improves application performance. Edit PHP configuration:
sudo nano /etc/php.iniConfigure OPcache settings:
opcache.enable=1
opcache.memory_consumption=256
opcache.max_accelerated_files=4000
opcache.revalidate_freq=2Application-level caching utilizes Laravel’s built-in cache system:
php artisan config:cache
php artisan route:cache
php artisan view:cache
php artisan optimizeDatabase query optimization involves regular maintenance and indexing:
OPTIMIZE TABLE assets;
ANALYZE TABLE assets;Security Hardening Measures
Regular update procedures maintain system security and functionality. Create automated update scripts for system packages:
#!/bin/bash
sudo dnf update -y
cd /var/www/snipe-it/
git pull origin master
composer install --no-dev --prefer-source
php artisan migrate --force
php artisan config:cacheSSL certificate installation encrypts data transmission:
sudo dnf install certbot python3-certbot-apache -y
sudo certbot --apache -d your-domain.comImplement access control through firewall rules and fail2ban integration:
sudo dnf install fail2ban -y
sudo systemctl enable fail2ban
sudo systemctl start fail2banMaintenance and Updates
Establish regular maintenance schedules including weekly log rotation, monthly security updates, and quarterly performance assessments. Database backup procedures should run daily with off-site storage:
#!/bin/bash
DATE=$(date +%Y%m%d_%H%M%S)
mysqldump -u snipeit_user -p snipeit_db > /backups/snipeit_$DATE.sql
find /backups/ -name "snipeit_*.sql" -mtime +30 -deleteSystem monitoring implementation using tools like Nagios, Zabbix, or Prometheus provides proactive issue detection. Configure alerts for disk space, memory usage, database performance, and application errors.
User training documentation ensures proper system utilization and reduces support requests. Create comprehensive guides covering asset creation, user management, reporting features, and troubleshooting procedures.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Snipe-IT. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Snipe-IT asset management system on your Fedora 42 Linux system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Snipe-IT website.