How To Install Thunderbird on Fedora 42

Mozilla Thunderbird stands as one of the most reliable and feature-rich email clients available for Linux users. This powerful, open-source application developed by Mozilla offers comprehensive email management capabilities, including support for multiple email accounts, advanced message filtering, encryption features, and extensive customization options through add-ons. For Fedora users, Thunderbird provides seamless integration with the Linux ecosystem while maintaining the security and stability that makes it a preferred choice for both personal and professional email management.
The installation process for Thunderbird on Fedora systems offers multiple approaches, each with distinct advantages depending on your specific needs and preferences. Whether you’re a system administrator seeking enterprise-level deployment or a home user looking for a straightforward setup, understanding the various installation methods will help you choose the most appropriate approach for your situation.
Prerequisites and System Requirements
Before beginning the installation process, ensure your Fedora 42 system meets the necessary requirements for optimal Thunderbird performance. Your system should have sufficient RAM and storage space to accommodate the application and its data files. Most modern Fedora installations will easily meet these requirements, but it’s essential to verify system compatibility.
Administrative privileges are required for most installation methods discussed in this guide. Ensure you have sudo access or root permissions to execute the installation commands. Additionally, maintain an active internet connection throughout the installation process, as most methods require downloading packages and dependencies from remote repositories.
Creating a system backup before installation is highly recommended, particularly if you’re upgrading from an existing email client or have important system configurations. This precautionary measure ensures you can restore your system to its previous state if any issues arise during the installation process.
Method 1: Installing Thunderbird via DNF Package Manager
The DNF package manager represents the most straightforward and recommended approach for installing Thunderbird on Fedora systems. This method provides excellent integration with the system’s package management infrastructure and ensures automatic security updates through the standard system update process.
System Update Process
Before installing any new software, update your system packages to their latest versions. This practice prevents potential compatibility issues and ensures you’re working with the most current software repositories. Execute the following command in your terminal:
sudo dnf upgrade --refreshThis command refreshes the package metadata and upgrades all installed packages to their latest available versions. The process may take several minutes depending on your system’s current state and internet connection speed.
DNF Installation Steps
Once your system is fully updated, install Thunderbird using the DNF package manager with this simple command:
sudo dnf install thunderbirdThe DNF package manager will automatically resolve dependencies and download the necessary files from Fedora’s official repositories. During installation, you’ll be prompted to confirm the installation by typing ‘y’ and pressing Enter. The entire process typically completes within a few minutes, depending on your internet connection speed.
Verify the installation by checking the installed package information:
dnf info thunderbirdThis command displays detailed information about the installed Thunderbird package, including its version number and installation status.
Advantages of DNF Installation
The DNF installation method offers several significant advantages. System integration is seamless, as the package manager handles all dependency resolution automatically. Updates are managed through the standard system update process, ensuring you receive security patches and feature updates without manual intervention.
Performance optimization is inherent with DNF installations, as the packages are compiled specifically for Fedora’s architecture and libraries. This optimization typically results in better performance compared to universal packaging formats.
Method 2: Installing Thunderbird via Flatpak
Flatpak provides an alternative installation method that offers unique advantages, particularly for users seeking application isolation and access to newer software versions. The Thunderbird Flatpak package is maintained directly by the Thunderbird team, ensuring timely updates and optimal compatibility.
Flatpak Setup and Configuration
If Flatpak isn’t already configured on your system, enable the Flathub repository using the following command:
sudo flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoThis command adds the Flathub repository to your system’s Flatpak configuration, providing access to thousands of applications including Thunderbird.
Verify Flatpak functionality by listing available remotes:
flatpak remotesYou should see Flathub listed among the available repositories.
Thunderbird Flatpak Installation
Install Thunderbird using Flatpak with this command:
flatpak install flathub org.mozilla.ThunderbirdThe installation process downloads the application and its runtime dependencies into a sandboxed environment. This approach provides enhanced security by isolating the application from the rest of your system.
Launch Thunderbird from the Flatpak installation using:
flatpak run org.mozilla.ThunderbirdAlternatively, you can launch it from your desktop environment’s application menu, where it will appear alongside other installed applications.
Handling Flatpak Migration Issues
Recent changes in Thunderbird’s Flatpak packaging may affect users upgrading from older installations. If you encounter issues with missing profiles or data after a Flatpak upgrade, the solution involves migrating your existing profile data to the new location.
Migrate your Thunderbird profile by copying the entire ~/.thunderbird folder to the new Flatpak location:
cp -r ~/.thunderbird ~/.var/app/org.mozilla.Thunderbird/.thunderbirdIf Thunderbird opens with a new profile instead of recognizing your existing data, use the profile manager to select the correct profile:
flatpak run org.mozilla.Thunderbird -PSelect your existing profile and check the “Use the selected profile without asking on startup” option to make it the default.
Method 3: Installing Thunderbird via Snap
Snap packages provide another universal packaging option for Thunderbird installation. This method offers good cross-distribution compatibility and automatic updates, making it suitable for users who prefer containerized applications.
Snap Setup on Fedora 42
Enable Snap support on your Fedora system by installing the snapd package:
sudo dnf install snapdCreate the necessary symbolic link for Snap functionality:
sudo ln -s /var/lib/snapd/snap /snapRestart your system to ensure all Snap services are properly initialized. This step is crucial for proper Snap functionality on Fedora systems.
Snap Installation Process
Install Thunderbird using Snap with this command:
sudo snap install thunderbirdThe Snap package manager handles the download and installation process automatically. Snap applications update automatically by default, ensuring you always have the latest stable version.
Verify the installation by checking the installed Snap packages:
snap listThunderbird should appear in the list of installed Snap applications.
Method 4: Manual Installation from Mozilla
For users requiring specific versions or maximum control over the installation process, manual installation directly from Mozilla’s servers provides the most flexibility. This method is particularly useful for testing pre-release versions or installing specific release channels.
System-wide Installation
Download the latest Thunderbird release from Mozilla’s official download page. The file will be in the format thunderbird-*.tar.bz2.
Navigate to your download directory and extract the archive:
cd ~/Downloads
tar xjf thunderbird-*.tar.bz2Move the extracted directory to the system location:
sudo mv thunderbird /optCreate a symbolic link for easy command-line access:
sudo ln -s /opt/thunderbird/thunderbird /usr/local/bin/thunderbirdDesktop Integration
Download the desktop file for proper application menu integration:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mozilla/sumo-kb/main/installing-thunderbird-linux/thunderbird.desktop -P /usr/local/share/applicationsThis desktop file ensures Thunderbird appears in your application menu and can be launched like any other installed application.
Verify the installation by checking the application binary location. Navigate to Help > Troubleshooting Information in Thunderbird, and confirm that the Application Binary path shows /opt/thunderbird/thunderbird-bin.
Post-Installation Configuration
After successfully installing Thunderbird, proper configuration ensures optimal performance and security. The initial setup process involves account configuration, security settings, and interface customization.
First Launch and Account Setup
Launch Thunderbird from your application menu or command line. The initial startup wizard guides you through the basic configuration process. Enter your email address and password when prompted, and Thunderbird will attempt to automatically configure your account settings.
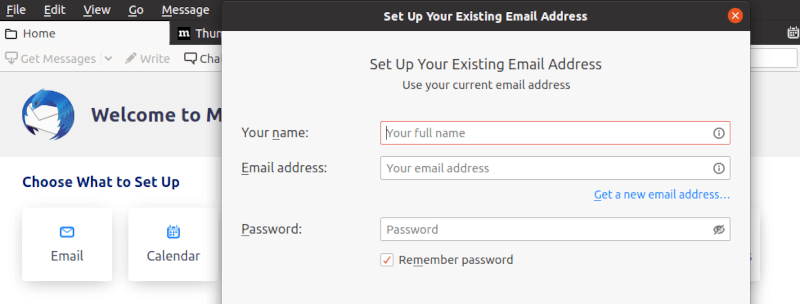
For manual configuration, click “Configure manually” and enter your email provider’s server settings. Common settings include IMAP/POP3 server addresses, port numbers, and security protocols. Consult your email provider’s documentation for specific configuration details.
Essential Configuration Options
Configure security and privacy settings by navigating to Edit > Preferences > Privacy & Security. Enable important security features such as automatic updates, phishing protection, and secure connections for email retrieval.
Install essential add-ons to enhance Thunderbird’s functionality. Popular add-ons include calendar integration, advanced message filtering, and productivity tools. Access add-ons through Tools > Add-ons and Themes.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with proper installation procedures, users may encounter various issues that require troubleshooting. Understanding common problems and their solutions helps ensure a smooth Thunderbird experience.
Installation Problems
Permission denied errors commonly occur when insufficient privileges are available for system-wide installations. Ensure you’re using sudo for commands that require administrative access, or consider user-specific installation methods.
Package dependency conflicts may arise when mixing different installation methods. Avoid installing Thunderbird through multiple package managers simultaneously, as this can create conflicts and duplicate application entries.
Network connectivity issues during download can interrupt the installation process. Verify your internet connection and try the installation again. For persistent network issues, consider downloading packages manually and installing them locally.
Post-Installation Issues
Generic icon display problems often occur with manual installations. Ensure the desktop file is properly configured and placed in the correct directory. The desktop file should specify the correct icon path and application executable location.
Profile migration issues can occur when switching between different installation methods. Use the profile manager to select the correct profile location, or manually copy profile data to the expected location for your installation method.
Performance issues may arise from various factors including add-on conflicts, large mailboxes, or system resource constraints. Troubleshoot performance problems by running Thunderbird in safe mode and gradually re-enabling features.
Updates and Maintenance
Regular updates are crucial for maintaining security and accessing new features. The update process varies depending on your installation method.
Updating Different Installation Types
DNF installations update automatically through the standard system update process:
sudo dnf upgrade thunderbirdFlatpak installations require manual updates or can be configured for automatic updates:
flatpak update org.mozilla.ThunderbirdSnap installations update automatically by default, but you can trigger manual updates:
sudo snap refresh thunderbirdManual installations require downloading and installing new versions following the same process used for initial installation.
Security Considerations
Monitor security advisories from Mozilla and your distribution’s security team. Keep your email client updated to protect against vulnerabilities and ensure compatibility with modern email security protocols.
Regular profile backups protect your email data and configurations. Export your profile periodically or use automated backup solutions to safeguard your important email data.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Thunderbird. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Thunderbird Mail on the Fedora 42 Linux system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Thunderbird website.