
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Timeshift on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS. For those of you who didn’t know, Timeshift is an application that will create a backup and restore point on our Linux Environment similar to the System Restore feature in Windows and the Time Machine tool in Mac OS. Timeshift protects your system by taking incremental snapshots of the file system at regular intervals. These snapshots can be restored at a later date to undo all changes to the system.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the Timeshift backup/restore application on Ubuntu 20.04 (Focal Fossa). You can follow the same instructions for Ubuntu 18.04, 16.04, and any other Debian-based distribution like Linux Mint.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Ubuntu 20.04, 18.04, 16.04, and any other Debian-based distribution like Linux Mint.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Timeshift on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Focal Fossa
Step 1. First, make sure that all your system packages are up-to-date by running the following apt commands in the terminal.
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
Step 2. Installing Timeshift on Ubuntu 20.04.
- Install Timeshift via default repository Ubuntu.
Timeshift packages are available in default repositories, run the following command to install them:
sudo apt install timeshift
- Install Timeshift via the official repository.
Now add the Timeshift repository to our Ubuntu system:
sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:teejee2008/ppa
Next, install the Timeshift using the below command:
sudo apt update sudo apt install timeshift
Step 3. Accessing Timeshift on Ubuntu.
Once successfully installing Timeshift on Ubuntu in the previous section, we now want to Create a Backup by using the Timeshift GUI. The first step is to use the application menu to search for the Timeshift application and launch it.
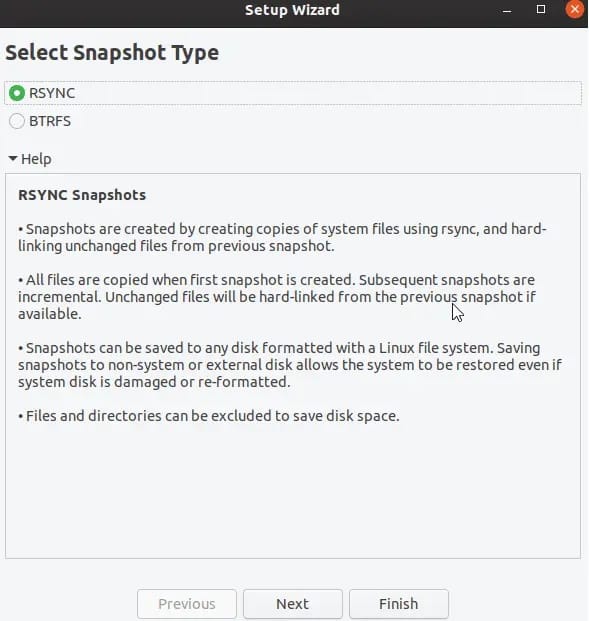
In the next step, you must select the snapshot type from the available options and click on Next.
- RSYNC – Rsync takes backup with the rsync command and also used hard links. Rsync backups are browsable using file managers.
- BTRFS – with this mode, timeshift uses in-built features of BTRFS & then to restore snapshots, BTRFS should be supported with the Ubuntu-type subvolume layout.
Timeshift also supports the command line to create and restore the backup. to create a backup, simply run the following command:
sudo timeshift --create --comments "Backup with CLI" --tags D
In tags, you can any of the following options:
–tags D stands for Daily Backup.
–tags W stands for Weekly Backup.
–tags M stands for Monthly Backup.
–tags O stands for On-demand Backup.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Timeshift. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Timeshift backup/restore application on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Focal Fossa system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Timeshift website.