How To Install UNetbootin on Debian 12

UNetbootin, short for Universal Netboot Installer, serves as a powerful, free, and open-source utility for creating bootable USB drives without burning a CD. Whether you’re looking to install a new Linux distribution or run a live environment from your USB stick, UNetbootin simplifies the process significantly on Debian 12 (Bookworm). This comprehensive guide walks you through multiple installation methods, usage techniques, and troubleshooting tips to ensure you can successfully create bootable media on your Debian system.
Understanding UNetbootin and Its Functionality
UNetbootin stands as one of the most popular tools for creating bootable USB drives across multiple platforms. This versatile application allows users to load various Linux distributions directly from the application or use locally stored ISO files to create bootable media.
The tool works by transferring the necessary boot files to your USB drive and configuring it to boot properly when connected to a computer. UNetbootin supports numerous Linux distributions out of the box, including Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora, and many others. This cross-platform utility works on Linux, Windows, and macOS, making it a universal solution for bootable media creation.
Key capabilities of UNetbootin include:
- Creating bootable USB drives from downloaded ISO files
- Directly downloading and installing Linux distributions
- Supporting multiple filesystem formats
- Configuring boot parameters
- Working with various system utilities and rescue tools
Important Considerations for Debian 12 Users
Before proceeding with UNetbootin installation on Debian 12, several important factors deserve attention. First and foremost, UNetbootin is not available in the official Debian 12 repositories. This absence aligns with Debian’s conservative approach to package inclusion and stability priorities.
Some Debian users have reported compatibility issues when using UNetbootin for creating bootable Debian media. In particular, some installations initiated with UNetbootin-created media have encountered errors during the installation process, such as problems reading from the installation source. These issues prompted some Debian community members to suggest alternatives like using official Debian methods for creating bootable media.
When working with Debian systems, the “Don’t Break Debian” philosophy remains paramount. This philosophy encourages users to rely on official repositories and recommended tools whenever possible to maintain system stability and security.
Method 1: Installing UNetbootin via Binary File
The most straightforward and recommended approach for installing UNetbootin on Debian 12 involves downloading and using the binary file directly from the project’s GitHub repository. This method avoids potential package conflicts and dependency issues.
Step 1: Download UNetbootin Binary File
Since UNetbootin isn’t available in Debian 12’s official repository, we need to download it from the UNetbootin GitHub page:
- Open your web browser and navigate to the UNetbootin Linux download page.
- Locate the appropriate binary file for your system architecture (32-bit or 64-bit)
- For most modern systems, download the 64-bit version (unetbootin-linux64-*.bin)
- The file will typically be saved to your Downloads folder
The binary file approach offers portability and simplicity, as it doesn’t require installing additional packages or adding external repositories to your system.
Step 2: Make Binary File Executable
Once downloaded, the binary file needs executable permissions before it can be run. Follow these commands in the terminal:
- Open Terminal by pressing Ctrl+Alt+T
- Navigate to your Downloads folder with:
cd Downloads - Make the binary file executable using the chmod command:
chmod +x ./unetbootin-linux64-*.bin - Verify that the file is now executable by checking its permissions:
ls -la unetbootin-linux64-*.binYou should see the execute (x) permission now enabled for the file.
Step 3: Run UNetbootin on Debian 12
With the executable permissions set, you can now run UNetbootin:
- Execute the binary with administrator privileges:
sudo ./unetbootin-linux64-*.bin - Enter your password when prompted
- The UNetbootin graphical interface should launch, allowing you to create bootable media
If you encounter a “command not found” error, verify you’re in the correct directory and that the filename matches the downloaded binary.
Method 2: Alternative Installation Methods
While the binary installation method is recommended for Debian 12, some users may prefer alternative approaches. These methods come with certain caveats and should be used with caution.
PPA Installation Method
Personal Package Archives (PPAs) provide an alternative installation method, though they’re generally more appropriate for Ubuntu-based systems than Debian:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:gezakovacs/ppa
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install unetbootinImportant warning: Using PPAs on Debian systems can potentially cause conflicts with Debian’s package management system and may lead to system instability. This approach contradicts Debian’s best practices and should only be considered in specific circumstances where the benefits outweigh the risks.
When to Consider Alternative Methods
These alternative installation methods might be appropriate in certain scenarios:
- When working in development or testing environments
- If you’re experienced with Debian package management and can handle potential conflicts
- When the binary installation method doesn’t work for your specific setup
- If you require integrations with other packages from the same PPA
For production systems or when system stability is critical, stick with the binary installation method described earlier.
Using UNetbootin on Debian 12
After successfully installing UNetbootin, you can use it to create bootable USB drives. The application offers a straightforward interface with several options.
Launching UNetbootin
To start UNetbootin, run the binary with administrator privileges as described earlier:
sudo ./unetbootin-linux64-*.binThe graphical interface provides two primary methods for creating bootable media:
Creating Bootable Media Using Distribution Selection
UNetbootin can download and install Linux distributions directly:
- Select “Distribution” in the main interface
- Choose your desired Linux distribution from the dropdown menu
- Select the appropriate version
- Choose “USB Drive” as the installation target
- Select your USB drive from the list (ensure you select the correct drive)
- Click “OK” to begin the download and installation process
This method is convenient when you don’t already have an ISO file and want to create bootable media in one step.
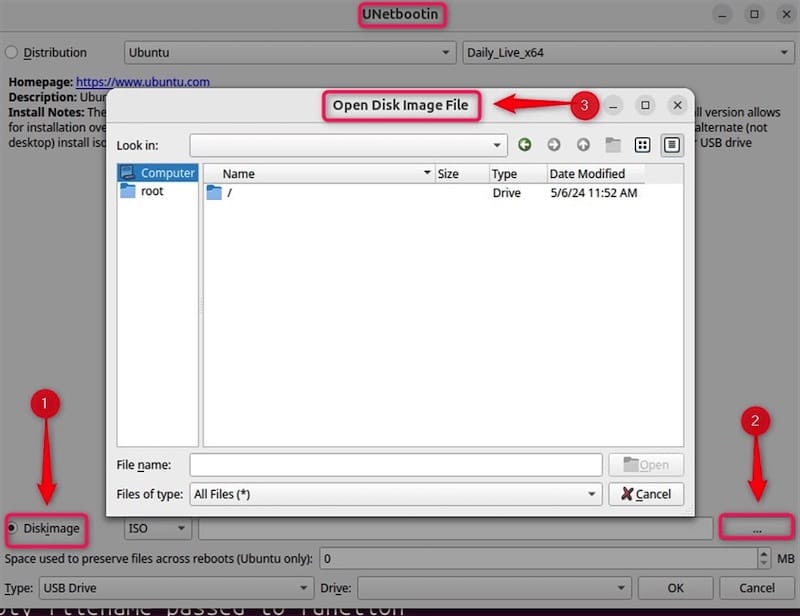
Creating Bootable Media Using Local ISO Files
If you already have an ISO file downloaded:
- Select “Disk image” in the main interface
- Click the browse button (…) and locate your ISO file
- Choose “USB Drive” as the installation target
- Select your USB drive from the dropdown list
- Click “OK” to begin creating the bootable USB
This method provides more flexibility and allows you to use custom or modified ISO files.
Creating a Debian 12 Bootable USB
To create a Debian 12 bootable USB drive specifically, follow these detailed steps:
Obtaining Official Debian 12 ISO Files
- Visit the official Debian website.
- Choose the appropriate ISO file for your needs:
- DVD image: Contains a more comprehensive set of packages
- CD image: Contains a minimal installation set
- netinst: Allows installation with an internet connection, downloading packages as needed
- Download the ISO file that matches your system architecture (amd64 for most modern systems)
Verifying Downloads with Checksums
Before creating your bootable media, verify the integrity of your downloaded ISO:
- Download the checksums file from the Debian website
- Open Terminal and navigate to the directory containing your ISO
- Verify the checksum with:
sha256sum -c SHA256SUMS - Proceed only if the verification succeeds
Configuring UNetbootin for Debian Installation
- Launch UNetbootin with administrator privileges
- Select the “Disk image” option
- Choose “ISO” and browse to your verified Debian 12 ISO file
- Select your USB drive as the target
- Click “OK” to begin creating the bootable USB
- Wait for the process to complete (this may take several minutes)
Testing and Verification
After creating your bootable USB:
- Restart your computer and boot from the USB drive (this typically requires pressing a key like F12, F2, or Esc during startup)
- Verify that the Debian installer launches correctly
- Test basic functionality before proceeding with a full installation
Some users have reported issues with UNetbootin-created Debian installation media. If you encounter problems, consider using one of the alternative tools discussed later in this article.
Recommended Alternatives for Debian 12
While UNetbootin serves many users well, several alternatives offer comparable or superior functionality, especially for Debian systems.
Balena Etcher: A Popular Alternative
Balena Etcher (formerly just Etcher) has gained popularity as an alternative to UNetbootin. This cross-platform tool offers several advantages:
- Simplified interface with fewer configuration options
- Better verification of written images
- Support for compressed images
- Generally more reliable with Debian images
Many users report that Balena Etcher works more consistently with Debian installation media than UNetbootin. Installation involves downloading the AppImage from the official website and making it executable.
Command-Line Alternatives
For users comfortable with the terminal, the dd command provides a reliable method for creating bootable USB drives:
sudo dd if=/path/to/debian.iso of=/dev/sdX bs=4M status=progressReplace /path/to/debian.iso with your ISO file path and /dev/sdX with your USB device (be extremely careful to identify the correct device).
Feature Comparison of Bootable USB Creation Tools
| Feature | UNetbootin | Balena Etcher | dd Command |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graphical Interface | Yes | Yes | No |
| Multiple OS Support | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Persistence Option | Yes | No | No |
| Verification | Limited | Built-in | Manual |
| Multiboot Support | No | No | No |
| Debian Compatibility | Variable | Good | Excellent |
For Debian-specific installations, MultiBootUSB and iVentoy also offer viable alternatives with unique features.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
UNetbootin users may encounter several common issues, particularly on Debian systems. Here are solutions to the most frequent problems:
Permission and Dependency Problems
Issue: “Permission denied” when running UNetbootin
Solution: Ensure you’re using sudo or running as root:
sudo ./unetbootin-linux64-*.binIssue: Missing dependencies
Solution: Install required packages:
sudo apt install libqt5core5a libqt5gui5 libqt5dbus5USB Drive Formatting Issues
Issue: USB drive not detected by UNetbootin
Solution: Format the drive as FAT32 before attempting to create bootable media:
- Open Terminal and identify your USB drive:
lsblk - Unmount the drive if mounted:
sudo umount /dev/sdX1 - Format as FAT32:
sudo mkfs.vfat -F 32 /dev/sdX1
Boot Failures and Solutions
Issue: USB drive created with UNetbootin won’t boot
Solutions:
- Reformat the USB drive as FAT32 and try again
- Try an alternative tool like Balena Etcher
- Check your BIOS/UEFI settings for USB boot options
- Verify that Secure Boot is disabled in UEFI systems
Distribution-Specific Challenges
Issue: “Cannot copy from CD” error during Debian installation
Solution: This is a known issue with UNetbootin and Debian. Alternatives include:
- Using Debian’s recommended USB creation method
- Trying NetBootCD instead of UNetbootin
- Using Balena Etcher to create the bootable media
Best Practices and Tips
To ensure success when using UNetbootin on Debian 12, follow these best practices:
USB Drive Selection Recommendations
- Use USB drives from reputable manufacturers
- Opt for USB 3.0 drives when possible for faster installations
- 8GB capacity is typically sufficient for most distributions
- Avoid using drives with important data, as they will be formatted
Data Backup Importance
Always back up any important data before:
- Formatting your USB drive
- Creating bootable media
- Installing a new operating system
Security Considerations
- Download ISO files only from official sources
- Verify checksums before creating bootable media
- Be cautious when granting administrative privileges to applications
Keeping Tools Updated
- Check for UNetbootin updates periodically
- Use the latest version of Debian 12 ISO files
- Update your system before creating bootable media
Congratulations! You have successfully installed UNetbootin. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing UNetbootin on Debian 12 “Bookworm” system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official UNetbootin website.