How To Install Zenmap on Linux Mint 22

Network security assessment has become increasingly crucial in today’s interconnected digital landscape. Zenmap, the official graphical user interface for the powerful Nmap network scanner, provides Linux Mint 22 users with an intuitive platform for conducting comprehensive network analysis and vulnerability assessments. This powerful tool transforms complex command-line operations into accessible visual workflows, making network scanning more efficient and user-friendly.
Installing Zenmap on Linux Mint 22 requires specific approaches due to recent changes in package availability and dependency management. The graphical interface offers significant advantages over command-line Nmap, including visual network topology mapping, scan result comparison capabilities, and profile-based scanning for consistent security assessments. Whether you’re a cybersecurity professional, network administrator, or security enthusiast, this comprehensive guide will walk you through multiple installation methods, configuration procedures, and best practices for using Zenmap effectively on Linux Mint 22.
Understanding Zenmap
Zenmap Core Features and Capabilities
Zenmap serves as more than just a graphical wrapper for Nmap. The application provides sophisticated scanning capabilities that include multi-port TCP and UDP protocol analysis, comprehensive IPv6 address scanning, and advanced MAC address spoofing detection mechanisms. Network administrators particularly value its service and daemon version detection features, which help identify potential security vulnerabilities across network infrastructure.
The scan result comparison functionality stands out as one of Zenmap’s most valuable features. This capability allows security professionals to track network changes over time, identify new services or devices, and monitor potential security incidents. The interactive network topology visualization provides clear insights into network architecture, helping teams understand complex network relationships and potential attack vectors.
Profile-based scanning ensures consistency across security assessments. Teams can create standardized scanning profiles for different network segments, compliance requirements, or specific security objectives. This approach maintains audit trails and ensures repeatable results across multiple scanning sessions.
System Requirements for Linux Mint 22
Linux Mint 22 users must meet specific hardware and software requirements for optimal Zenmap performance. The system requires minimum 2GB RAM for basic scanning operations, though 4GB or more is recommended for intensive network analysis tasks. Administrative privileges through sudo access are essential for installation and many scanning operations.
Python GTK dependencies form the foundation of Zenmap’s graphical interface. Linux Mint 22’s compatibility with Ubuntu 22.04 packages generally ensures smooth operation, but users must verify specific dependency versions during installation. Network connectivity is crucial not only for scanning operations but also for downloading installation packages and updates.
Storage requirements are minimal, with Zenmap requiring less than 50MB disk space. However, scan results and historical data can accumulate quickly, particularly in enterprise environments conducting regular security assessments.
Pre-Installation Preparation
System Updates and Package Management
Proper system preparation significantly reduces installation complications and ensures optimal performance. Begin by updating your Linux Mint 22 system using the command sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade. This process refreshes package repositories and installs critical security updates that may affect Zenmap functionality.
Repository source verification prevents installation issues related to package availability. Check your /etc/apt/sources.list file to ensure official Ubuntu and Linux Mint repositories are correctly configured. Network connectivity testing using basic ping commands helps identify potential download issues before beginning the installation process.
Package manager integrity verification through sudo apt-get check identifies and resolves any existing dependency conflicts that might interfere with Zenmap installation. This proactive approach prevents complex troubleshooting scenarios later in the process.
Installing Prerequisites and Dependencies
The Nmap base package provides essential functionality that Zenmap requires for operation. Install it using sudo apt install nmap. This command downloads and configures the core scanning engine that powers Zenmap’s graphical interface.
Python GTK installation enables the graphical user interface components. Linux Mint 22 typically includes most required Python libraries, but Zenmap specifically requires Python 2.x GTK bindings that may not be available in default repositories. The build-essential package becomes necessary if you choose source compilation: sudo apt install build-essential.
Network utilities and development libraries support advanced Zenmap features. Install additional tools using sudo apt install git wget curl to facilitate package downloads and version control operations. Verification of installed components through nmap --version confirms successful base installation before proceeding with Zenmap-specific steps.
Installation Method 1: Manual .deb Package Installation
Understanding the Manual Installation Approach
Manual .deb package installation represents the most reliable method for installing Zenmap on Linux Mint 22. Recent Linux distributions have removed Zenmap from official repositories due to Python 2 dependency concerns and maintenance challenges. This approach provides direct control over the installation process while ensuring compatibility with your specific system configuration.
Security considerations require careful attention when downloading packages from external sources. Always verify package integrity using checksums and download only from trusted repositories or official sources. The manual method offers advantages including version control, dependency management, and the ability to troubleshoot specific installation issues.
Step-by-Step Installation Process
Step 1: Installing Python GTK Dependencies
Python GTK dependencies form the foundation of Zenmap’s graphical interface. Download the required package using:
wget http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/universe/p/pygtk/python-gtk2_2.24.0-5.1ubuntu2_amd64.debInstall the dependency package with:
sudo apt install ./python-gtk2_2.24.0-5.1ubuntu2_amd64.debThis command handles dependency resolution automatically while preserving system stability. Monitor the installation output for any error messages or dependency conflicts that require additional attention.
Step 2: Downloading Zenmap .deb Package
Acquire the Zenmap package from the Ubuntu archive:
wget http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/universe/n/nmap/zenmap_7.60-1ubuntu5_all.debPackage verification ensures installation integrity. Use ls -la zenmap_7.60-1ubuntu5_all.deb to confirm successful download and verify file size matches expected values. The package size should be approximately 600KB for the standard distribution.
Step 3: Installing Zenmap Package
Execute the installation command:
sudo apt install ./zenmap_7.60-1ubuntu5_all.debThe APT package manager automatically resolves remaining dependencies while installing Zenmap. This process typically takes 2-3 minutes depending on system performance and network connectivity. Watch for any dependency warnings that might require manual intervention.
Step 4: Installation Verification
Test the installation using zenmap --version. This command should return version information and confirm successful installation. Additionally, verify GUI accessibility by running sudo zenmap from the terminal. The graphical interface should launch without error messages or missing component warnings.
Post-Installation Configuration
Desktop shortcut creation enhances user accessibility. Create a desktop launcher by copying the system-wide desktop file: cp /usr/share/applications/zenmap.desktop ~/Desktop/. Modify the launcher properties to include necessary permissions and execution parameters.
Permission configuration optimizes Zenmap functionality. Many scanning operations require root privileges, so configure sudo access appropriately. Consider creating specific user groups for network scanning activities to maintain security while enabling necessary functionality.
Initial launch procedures should include basic connectivity testing. Run simple ping scans against local network addresses to verify proper operation before attempting complex security assessments.
Installation Method 2: APT Package Manager (Alternative Approach)
APT Installation Overview
The APT package manager method offers simplicity but faces limitations with recent Linux Mint versions. Official repositories have removed Zenmap packages due to Python 2 deprecation and security maintenance concerns. This method works best for users with access to custom repositories or older package archives.
Understanding when to use APT versus manual installation depends on your specific requirements and system configuration. APT installation provides automatic updates and dependency management but may result in outdated Zenmap versions or installation failures on newer systems.
Installation Commands and Process
System updates prepare the package manager for Zenmap installation:
sudo apt-get updateAttempt Zenmap installation through APT:
sudo apt-get install zenmapVersion verification confirms successful installation:
zenmap --versionTroubleshoot “package not found” errors by checking repository sources. Alternative repository sources may include third-party PPAs or custom repositories maintained by security communities. Exercise caution when adding external repositories to maintain system security.
Handling Installation Conflicts
Dependency conflicts with existing packages require careful resolution. Use apt list --installed | grep nmap to identify existing Nmap installations that might conflict with Zenmap requirements. Multiple Nmap installations can coexist but may require specific configuration adjustments.
Package removal procedures help clean conflicting installations. Use sudo apt remove nmap zenmap followed by sudo apt autoremove to completely remove problematic packages before attempting fresh installation. This approach resolves most dependency-related installation issues.
Installation Method 3: Source Code Compilation
When to Choose Source Installation
Source code compilation offers maximum flexibility and access to latest Zenmap features. This method suits advanced users who require specific configuration options or need to modify Zenmap functionality for specialized environments. Development teams often prefer source installation for customization purposes.
Benefits include access to cutting-edge features, custom compilation flags, and complete control over the installation process. However, source compilation requires additional development tools and technical expertise compared to package-based installation methods.
Source Compilation Process
Prerequisites Installation:
Install essential development tools:
sudo apt install build-essential python2-dev libgtk2.0-devThese packages provide compilation tools and library headers necessary for building Zenmap from source. Additional development libraries may be required depending on your specific configuration and feature requirements.
Download and Extraction:
Download the latest Nmap source package:
wget https://nmap.org/dist/nmap-7.93.tar.bz2
tar -xjf nmap-7.93.tar.bz2
cd nmap-7.93Archive extraction creates the build directory containing source code and configuration scripts. Navigate to the extracted directory to begin the compilation process.
Configuration and Compilation:
Execute the configuration script:
./configure --with-zenmapBegin compilation:
makeInstall the compiled software:
sudo make installThis compilation process typically requires 10-15 minutes depending on system performance. Monitor output for compilation errors that might indicate missing dependencies or configuration issues.
Source Installation Troubleshooting
Common compilation errors often relate to missing development libraries or incompatible Python versions. Address missing dependencies by installing additional development packages as indicated by error messages. Build environment optimization through compiler flags can resolve performance-related compilation issues.
Version conflicts between Python 2 and Python 3 frequently cause compilation problems. Ensure Python 2 development headers are available and properly configured for Zenmap compilation requirements.
Using Zenmap on Linux Mint 22
Launching Zenmap
Root access requirements necessitate launching Zenmap with elevated privileges: sudo zenmap. This approach ensures proper network access and scanning capabilities. Desktop launcher configuration should include appropriate privilege escalation to avoid repeated password prompts during regular usage.
Command-line versus GUI access methods offer different advantages. Command-line launch provides direct control and debugging information, while GUI access through desktop menus offers convenience for regular users. Configure your preferred access method based on usage patterns and security requirements.
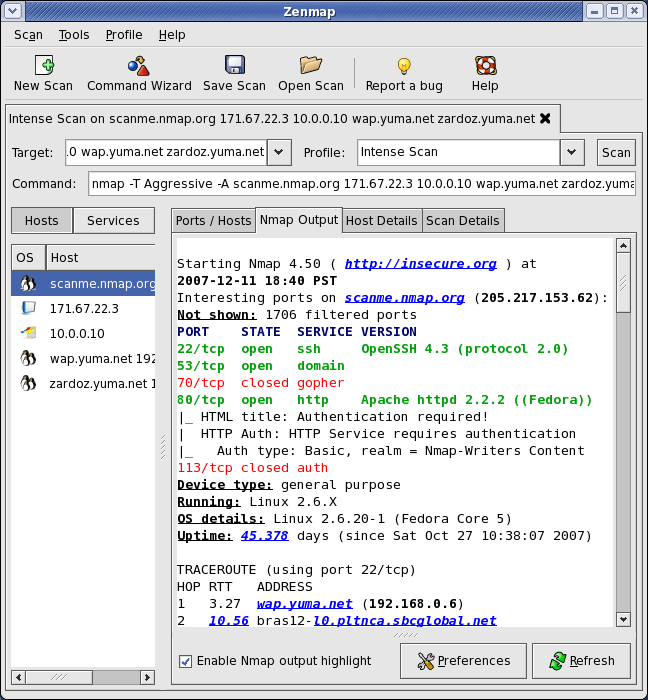
Basic Scanning Operations
Target specification supports various input formats including individual IP addresses, hostname resolution, and network ranges. Common target formats include 192.168.1.1, example.com, and 192.168.1.0/24 for network ranges. Proper target specification ensures comprehensive coverage while avoiding unnecessary network traffic.
Profile selection streamlines scanning operations through predefined configurations. Quick scan profiles provide rapid host discovery suitable for initial network reconnaissance. Intense scan profiles offer comprehensive analysis including service detection, version identification, and vulnerability assessment. Ping scan profiles focus on connectivity testing without invasive port scanning operations.
Command builder interface usage simplifies complex scan configuration. The graphical interface translates user selections into appropriate Nmap command-line parameters, making advanced scanning accessible to users without extensive command-line expertise. Real-time scan progress monitoring provides immediate feedback on scanning operations and estimated completion times.
Advanced Features and Functionality
Scan result analysis requires understanding of output formats and security implications. Zenmap presents results through multiple views including host lists, service summaries, and detailed port information. Network topology visualization capabilities provide graphical representations of discovered network relationships.
Scan comparison functionality enables security monitoring through historical analysis. Compare current scan results with previous assessments to identify new services, changed configurations, or potential security incidents. This capability proves invaluable for ongoing security monitoring and compliance reporting.
Profile creation and management support customized scanning workflows. Create organization-specific profiles that incorporate security policies, compliance requirements, and operational procedures. Result export options include XML and text formats compatible with other security tools and reporting systems.
Troubleshooting Common Installation Issues
Package Installation Problems
“Package not found” errors typically indicate repository configuration issues or package availability problems. Verify repository sources using sudo apt update and check internet connectivity. Repository source configuration issues may require manual editing of /etc/apt/sources.list or adding appropriate PPA sources.
Dependency conflicts arise when existing packages prevent Zenmap installation. Use apt list --upgradable to identify potential conflicts and resolve them through selective package updates. Permission denied errors during installation usually indicate insufficient sudo privileges or incorrect user group membership.
Internet connectivity troubleshooting becomes necessary when downloads fail repeatedly. Test connectivity using ping google.com and verify DNS resolution through nslookup. Proxy configurations in corporate environments may require additional APT configuration adjustments.
Runtime and Usage Issues
“Command not found” errors suggest PATH configuration problems or incomplete installation. Verify Zenmap installation using which zenmap and check executable permissions. Python compatibility issues between Python 2 and Python 3 installations frequently cause runtime failures.
GUI display problems often relate to X11 forwarding configuration or display server issues. Ensure proper DISPLAY variable configuration when using SSH connections or remote access. Permission errors during scanning operations typically require proper sudo configuration or user group membership adjustments.
Wayland compatibility considerations affect graphical applications on newer Linux distributions. Some scanning operations may require switching to X11 sessions for optimal compatibility with Zenmap’s GTK interface.
System-Specific Linux Mint 22 Issues
Desktop environment integration problems may prevent proper menu item creation or icon display. Manually refresh desktop database using sudo update-desktop-database to resolve launcher integration issues. Snap package conflicts can interfere with traditional APT installations.
Path configuration and environment variable settings affect command-line access to Zenmap. Verify /usr/local/bin inclusion in system PATH and adjust shell configuration files as necessary. Session management in different desktop environments may require specific configuration adjustments.
Security Considerations and Best Practices
Ethical and Legal Usage Guidelines
Network scanning ethics require proper authorization before conducting security assessments. Obtain explicit written permission from network owners before scanning any systems outside your administrative control. Corporate policy adherence ensures compliance with organizational security procedures and legal requirements.
Responsible disclosure principles apply when discovering vulnerabilities during security assessments. Follow established protocols for reporting security issues to appropriate parties while avoiding public disclosure of sensitive information. Legal compliance varies by jurisdiction and requires understanding of local cybersecurity laws and regulations.
Security Configuration Recommendations
User privilege management through proper sudo configuration minimizes security risks while enabling necessary functionality. Create dedicated user accounts for security testing activities and limit access to production systems. Network segmentation for testing environments prevents accidental scanning of critical infrastructure.
Scan frequency limitations help avoid overwhelming network resources and triggering security alerts. Implement rate limiting for automated scanning operations and coordinate assessment schedules with network administrators. Log management and audit trail maintenance support forensic analysis and compliance reporting requirements.
Data Protection and Privacy
Scan result confidentiality requires proper storage security and access controls. Encrypt sensitive scan data and implement appropriate retention policies for security assessment results. Personal information protection during network discovery ensures compliance with privacy regulations including GDPR and similar data protection laws.
Consider anonymization techniques for scan results when sharing information across teams or with external parties. Implement data classification schemes that appropriately protect sensitive network information while enabling necessary security analysis activities.
Advanced Configuration and Optimization
Performance Tuning
Scan performance optimization involves balancing thoroughness with network impact considerations. Adjust timing templates using Zenmap’s advanced options to match network characteristics and scanning objectives. Parallel scanning configuration can significantly reduce assessment time for large network ranges.
Memory management becomes important during extensive scanning operations. Monitor system resources during large scans and adjust scan parameters to prevent system overload. Network bandwidth considerations help maintain operational network performance during security assessments.
Integration with Security Workflows
Security information and event management (SIEM) integration enables automated processing of Zenmap scan results. Configure output formats compatible with your security monitoring infrastructure for seamless data flow. Vulnerability management integration supports risk assessment and remediation tracking processes.
Compliance reporting automation reduces manual effort in security assessment documentation. Develop templates and scripts that transform Zenmap output into required compliance formats for various regulatory frameworks including PCI DSS, SOX, and industry-specific requirements.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Zenmap. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Zenmap network scanning and analysis tool on your Linux Mint 22 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Zenmap website.