How To Install Apache Guacamole on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Apache Guacamole on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS. For those of you who didn’t know, Apache Guacamole is a powerful open-source remote desktop gateway that allows users to access their desktops from anywhere using a web browser. It supports multiple protocols, including VNC, RDP, and SSH, making it a versatile solution for remote access. Guacamole provides a sleek, HTML5-based web client that is compatible with most modern web browsers, eliminating the need for additional plugins or software installations on the client side.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the Apache Guacamole remote desktop application on Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish). You can follow the same instructions for Ubuntu 22.04 and any other Debian-based distribution like Linux Mint, Elementary OS, Pop!_OS, and more as well.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Ubuntu 22.04, 20.04, and any other Debian-based distribution like Linux Mint.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- An active internet connection. You’ll need an internet connection to download the necessary packages and dependencies for Apache Guacamole.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Apache Guacamole on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Jammy Jellyfish
Step 1. To ensure that your Ubuntu 22.04 server has the latest packages and security updates, start by updating the package list and upgrading any installed packages. Open a terminal and run the following commands:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade sudo apt install wget apt-transport-https gnupg2 software-properties-common
Step 2. Install Dependencies.
Apache Guacamole requires several dependencies to function correctly, including Java, Tomcat, and various libraries:
sudo apt install libcairo2-dev libjpeg62-turbo-dev libpng-dev libossp-uuid-dev freerdp2-dev libpango1.0-dev libssh2-1-dev libtelnet-dev libvncserver-dev libpulse-dev libssl-dev libvorbis-dev libwebp-dev -y
Step 3. Installing Java.
Before installing of Apache Tomcat Server, we set up an open-source Java Development Kit on your Ubuntu system:
sudo apt install openjdk-11-jdk
Confirm installation by checking the Java version:
java --version
For additional resources on installing Java, read the post below:
Step 4. Installing MySQL Server.
Guacamole requires a database to store user information and connection configurations.
sudo apt install mysql-server
Secure the MySQL installation:
sudo mysql_secure_installation
Next, Create the Guacamole database and user:
sudo mysql -u root -p CREATE DATABASE guacamole_db; CREATE USER 'guacamole_user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'strong_your_password'; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON guacamole_db.* TO 'guacamole_user'@'localhost'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; EXIT;
Step 5. Installing Apache Tomcat on Ubuntu 22.04.
By default, the Apache Tomcat is available on Ubuntu 22.04 base repository. First, we check the availability of the Apache Tomcat package in the repository:
sudo apt-cache search tomcat
Now run the following command below to install the last version of the Apache Tomcat package to your Ubuntu system:
sudoinstall tomcat9 tomcat9-admin tomcat9-common tomcat9-user
Step 6. Installing Apache Guacamole on Ubuntu 22.04.
By default, Apache Guacamole is not available on Ubuntu 22.04 base repository. Now run the following command below to download the latest version of Apache Guacamole to your Ubuntu system:
wget https://downloads.apache.org/guacamole/1.5.5/source/guacamole-server-1.5.5.tar.gz
Next, extract the downloaded file:
tar xzf guacamole-server-1.5.5.tar.gz
Now change the Guacamole server source code directory and run the following commands to check that all requirements are met:
cd guacamole-server-1.5.5 CFLAGS=-Wno-error ./configure --with-systemd-dir=/etc/systemd/system/
For more configure options, run, ./configure --help.
Output:
------------------------------------------------
guacamole-server version 1.5.5
------------------------------------------------
Library status:
freerdp2 ............ yes
pango ............... yes
libavcodec .......... yes
libavformat.......... yes
libavutil ........... yes
libssh2 ............. yes
libssl .............. yes
libswscale .......... yes
libtelnet ........... yes
libVNCServer ........ yes
libvorbis ........... yes
libpulse ............ yes
libwebsockets ....... yes
libwebp ............. yes
wsock32 ............. no
Protocol support:
Kubernetes .... yes
RDP ........... yes
SSH ........... yes
Telnet ........ yes
VNC ........... yes
Services / tools:
guacd ...... yes
guacenc .... yes
guaclog .... yes
FreeRDP plugins: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/freerdp
Init scripts: no
Systemd units: /etc/systemd/system/
Type "make" to compile guacamole-server.
After that, compile and install the Guacamole Server on Ubuntu 22.04:
sudo make sudo make install sudo ldconfig
Once installed, the commands below can be used to start and enable it so that it automatically startup when you boot up the machine:
sudo systemctl enable guacd sudo systemctl start guacd
Step 7. Installing Guacamole Client.
Now we run the commands below to download the Guacamole client:
mkdir /etc/guacamole wget https://downloads.apache.org/guacamole/1.5.5/binary/guacamole-1.5.5.war -O /etc/guacamole/guacamole.war
Next, create a symbolic link of the Guacamole client to the Tomcat webapps directory:
ln -s /etc/guacamole/guacamole.war /var/lib/tomcat9/webapps/
Now we restart Tomcat and guacd to deploy the new web application:
sudo systemctl restart tomcat9 sudo systemctl restart guacd
Step 8. Configure Apache Guacamole.
After the installation, Guacamole has two major configuration files: /etc/guacamole which is referenced by the GUACAMOLE_HOME environment variable and /etc/guacamole/guacamole.properties which is the main configuration file used by Guacamole and its extensions.
There are also guacamole extensions and library configurations. You need to create the directories for these configs;
mkdir /etc/guacamole/{extensions,lib}
Set the guacamole home directory environment variable and add it to /etc/default/tomcat9 the configuration file:
echo "GUACAMOLE_HOME=/etc/guacamole" >> /etc/default/tomcat9
Now we configure Guacamole server connections. You need to define how to Guacamole client will connect to the Guacamole server under the /etc/guacamole/guacamole.properties configuration file:
nano /etc/guacamole/guacamole.properties
Add these lines:
guacd-hostname: localhost guacd-port: 4822 user-mapping: /etc/guacamole/user-mapping.xml auth-provider: net.sourceforge.guacamole.net.basic.BasicFileAuthenticationProvider
Save the file, then link the Guacamole configurations directory to the Tomcat servlet directory as shown below:
ln -s /etc/guacamole /usr/share/tomcat9/.guacamole
Next, configure the Guacamole authentication method:
nano /etc/guacamole/user-mapping.xml
Add the configuration below:
<user-mapping>
<!-- Per-user authentication and config information -->
<!-- A user using md5 to hash the password
guacadmin user and its md5 hashed password below is used to
login to Guacamole Web UI-->
<authorize
username="idroot"
password="4f4def3b5aa100d61d1207deb882cf46"
encoding="md5">
<!-- First authorized Remote connection -->
<connection name="Ubuntu-Server">
<protocol>ssh</protocol>
<param name="hostname">192.168.77.21</param>
<param name="port">22</param>
</connection>
<!-- Second authorized remote connection -->
<connection name="Windows 11">
<protocol>rdp</protocol>
<param name="hostname">192.168.77.20</param>
<param name="port">3389</param>
<param name="username">chedelics</param>
<param name="ignore-cert">true</param>
</connection>
</authorize>
</user-mapping>
Then, generate the MD5 hash of passwords for a user you are going to use to log into the Guacamole web user interface:
echo -n password | openssl md5 printf '%s' password | md5sum
If you need to explicitly define usernames and passwords, add the parameters:
<param name="username">USERNAME</param> <param name="password">PASSWORD</param>
Save and exit the configuration file, then restart both Tomcat and guacd to realize the changes made:
sudo systemctl restart tomcat9 guacd
Step 9. Configure Firewall.
Now we set up an Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW) with Guacamole to allow public access on default web ports 8080:
sudo ufw allow OpenSSH sudo ufw allow 8080/tcp sudo ufw enable
Step 10. Accessing Apache Guacamole Web Interface.
Once successfully installed, open your web browser and access Apache Guacamole using the URL http://Your-IP-address:8080/guacamole. You will be redirected to the following page:
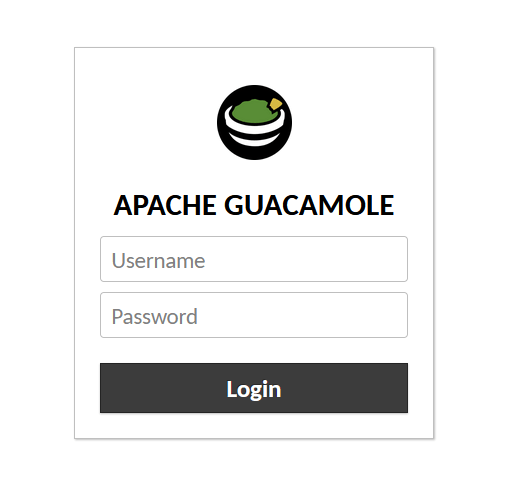
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Apache Guacamole. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Apache Guacamole remote desktop application on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Jammy Jellyfish system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Apache website.