
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install FileRun on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS. For those of you who didn’t know, FileRun is a web-based file and sharing application. It is a very good alternative to Google Drive self-hosted. It allows you to share and sync files, access them via WebDAV, and even connect to them with the Nextcloud mobile app.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of FileRun on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa). You can follow the same instructions for Ubuntu 18.04, 16.04, and any other Debian-based distribution like Linux Mint.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Ubuntu 20.04, 18.04, 16.04, and any other Debian-based distribution like Linux Mint.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install FileRun on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Focal Fossa
Step 1. Before we install any software, it’s important to make sure your system is up to date by running the following apt commands in the terminal:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
Step 2. Installing the LAMP stack.
A Ubuntu 20.04 LAMP server is required. If you do not have LAMP installed, you can follow our guide here. After that, we create a PHP configuration file for FileRun:
nano /etc/php/7.4/apache2/conf.d/filerun.ini
Add the following configuration:
expose_php = Off error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE display_errors = Off display_startup_errors = Off log_errors = On ignore_repeated_errors = Off allow_url_fopen = On allow_url_include = Off variables_order = "GPCS" allow_webdav_methods = On memory_limit = 128M max_execution_time = 300 output_buffering = Off output_handler = "" zlib.output_compression = Off zlib.output_handler = "" safe_mode = Off register_globals = Off magic_quotes_gpc = Off upload_max_filesize = 20M post_max_size = 20M enable_dl = Off disable_functions = "" disable_classes = "" session.save_handler = files session.use_cookies = 1 session.use_only_cookies = 1 session.auto_start = 0 session.cookie_lifetime = 0 session.cookie_httponly = 1 date.timezone = "UTC"
Save and close the file then restart the Apache service to apply the changes:
sudo systemctl reload apache2
Step 3. Installing FileRun on Ubuntu 20.04.
By default, FileRun is not available on Ubuntu 20.04 base repository. Now we run the commands below to download the latest version of FileRun from the official page:
wget -O FileRun.zip https://filerun.com/download-latest
Next, unzip the downloaded file using the following command:
unzip FileRun.zip -d /var/www/html/filerun/
We will need to change some folders permissions:
chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/filerun chmod -R 755 /var/www/html/filerun
Step 4. Configuring MariaDB.
By default, MariaDB is not hardened. You can secure MariaDB using the mysql_secure_installation script. you should read and below each step carefully which will set a root password, remove anonymous users, disallow remote root login, and remove the test database and access to secure MariaDB:
mysql_secure_installation
Configure it like this:
- Set root password? [Y/n] y - Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y - Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y - Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y - Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
Next, we will need to log in to the MariaDB console and create a database for the FileRun. Run the following command:
mysql -u root -p
This will prompt you for a password, so enter your MariaDB root password and hit Enter. Once you are logged in to your database server you need to create a database for FileRun installation:
CREATE DATABASE prestashopdb; CREATE USER 'prestashopuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'Your-Strong-Passwd'; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON `prestashopdb`.* TO 'prestashopuser'@'localhost'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Step 5. Configuring Apache webserver.
Now create an Apache virtual host configuration file for FileRun. You can create it with the following command below:
nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/filerun.conf
Add the following lines:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName your-domian.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/filerun
<Directory "/var/www/html/filerun">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/filerun.error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/filerun.access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
Save and close the file then restart Apache with the following command:
sudo a2ensite filerun.conf sudo a2enmod rewrite sudo systemctl restart apache2
Step 6. Set up HTTPS.
We should enable a secure HTTPS connection on PrestaShop. We can obtain a free TLS certificate from Let’s Encrypt. Install Let’s Encrypt client (Certbot) from Ubuntu 20.04 repository:
sudo apt install certbot python3-certbot-apache
Next, run the following command to obtain a free TLS certificate using the Apache plugin:
certbot --apache -d your-domian.com
You will be asked to provide your email and accept the term of service:
Enabled Apache rewrite module Redirecting vhost in /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/filerun.conf to ssl vhost in /etc/apache2/sites-available/filerun-le-ssl.conf - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Congratulations! You have successfully enabled https://your-domain.com You should test your configuration at: https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=your-domain.com - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - IMPORTANT NOTES: - Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/your-domain.com/fullchain.pem Your key file has been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/your-domain.com/privkey.pem Your cert will expire on 2022-09-21. To obtain a new or tweaked version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot again with the "certonly" option. To non-interactively renew *all* of your certificates, run "certbot renew" - If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by: Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le
If the test is successful, reload Apache for the change to take effect:
sudo apache2ctl -t sudo systemctl reload apache2
Step 7. Configure Firewall.
By default, the UFW firewall is enabled on Ubuntu. Depending on your Apache virtual host configuration file, open ports 80 and 443 to allow HTTP and HTTPS traffic:
sudo ufw allow 80/tcp sudo ufw allow 443/tcp sudo ufw reload
Step 8. Accessing FileRun Web Interface.
Once successfully installed, open your web browser and access the FileRun web interface using the URL https://your-domain.com. You should see the following page:
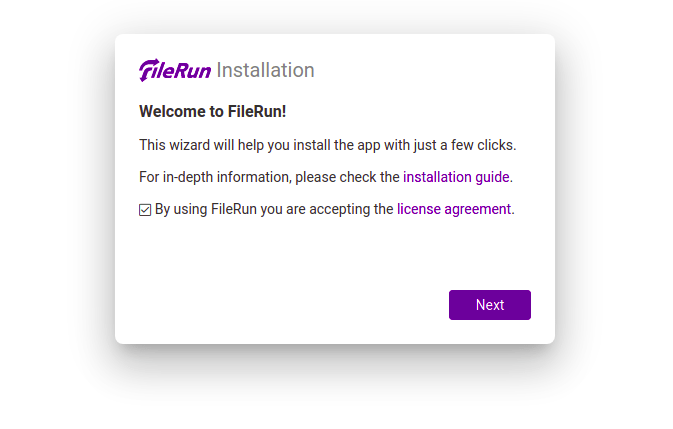
Congratulations! You have successfully installed FileRun. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the latest version of FileRun on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official FileRun website.