
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Gitea on Debian 11. For those of you who didn’t know, Gitea is an open-source Git service written in the Go language. It is a version control platform similar to GitHub. It is robust, scalable, and offers many features including issues and time tracking, repository branching, file locking, tagging, merging, and many others. Since Gitea was created using the Go language, it supports a lot of operating systems including Linux, macOS, and Windows, on architectures like amd64, i386, ARM, PowerPC, and others.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you through the step-by-step installation of the Gitea on a Debian 11 (Bullseye).
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Debian 11 (Bullseye).
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Gitea on Debian 11 Bullseye
Step 1. Before we install any software, it’s important to make sure your system is up to date by running the following apt commands in the terminal:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
Step 2. Installing MariaDB.
Gitea uses a MariaDB as a database backend. now we add MariaDB signing key and APT repository:
wget https://mariadb.org/mariadb_release_signing_key.asc sudo chmod -c 644 mariadb_release_signing_key.asc sudo mv -vi mariadb_release_signing_key.asc /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/
Next, add the MariaDB repository manually on your Debian system:
echo "deb [arch=amd64,arm64,ppc64el] \ https://ftp.ubuntu-tw.org/mirror/mariadb/repo/10.6/debian \ bullseye main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mariadb.list
Once done, install MariaDB using the following command below:
sudo apt update sudo apt install mariadb-server
Confirm the installation of MariaDB by checking the version and build:
mariadb --version
Now run the following commands to start MariaDB and enable it to automatically start on system reboot:
sudo systemctl start mariadb sudo systemctl enable mariadb
Secure MariaDB installation.
By default, MariaDB is not hardened. You can secure MariaDB using the mysql_secure_installation script. you should read and below each step carefully which will set a root password, remove anonymous users, disallow remote root login, and remove the test database and access to secure MariaDB:
mysql_secure_installation
Configure it like this:
- Set root password? [Y/n] y - Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y - Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y - Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y - Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
You can now connect to the MariaDB server using the new password:
mysql -u root -p
Once you are connected, create a database and user for Gitea with the following command below:
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE gitea; MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON gitea.* TO 'gitea'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'your-strong-password'; MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES; MariaDB [(none)]> QUIT;
Step 3. Installing Git.
By default, Git is available in the Debian Bullseye repository, Run the following command below to install it:
sudo apt install git
Verify the installation by printing the Git version:
git --version
Step 4. Create User for Gitea.
Add a Git user account for Gitea using the following commands:
adduser --system --shell /bin/bash --gecos 'Git Version Control' --group --disabled-password --home /opt/git git
Step 5. Installing Gitea on Debian 11.
Now we download the latest version of Gitea from the GitHub page:
curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/go-gitea/gitea/releases/latest |grep browser_download_url | cut -d '"' -f 4 | grep '\linux-amd64$' | wget -i -
Next, move the Gitea binary to the system path:
mv gitea-*-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/gitea
After that, set executable permission to the Gitea binary:
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/gitea
Verify the Gitea version:
gitea --version
Next, you will need to create a directory structure for Gitea. You can create it with the following command below:
mkdir -p /etc/gitea /var/lib/gitea/{custom,data,indexers,public,log}
Then, set proper permission and ownership with the following command:
chown git:git /var/lib/gitea/{data,indexers,log}
chmod 750 /var/lib/gitea/{data,indexers,log}
chown root:git /etc/gitea
chmod 770 /etc/gitea
Step 6. Create Gitea Systemd File.
Now we create systemd for Gitea services on /etc/systemd/system/gitea.service:
nano /etc/systemd/system/gitea.service
Add the following line:
[Unit] Description=Gitea (Git with a cup of tea) After=syslog.target After=network.target After=mysql.service [Service] LimitMEMLOCK=infinity LimitNOFILE=65535 RestartSec=2s Type=simple User=git Group=git WorkingDirectory=/var/lib/gitea/ ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/gitea web -c /etc/gitea/app.ini Restart=always Environment=USER=git HOME=/opt/git GITEA_WORK_DIR=/var/lib/gitea [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save and close, then reload the systemd daemon with the following command:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl enable gitea sudo systemctl start gitea
Step 7. Configure Nginx for Gitea.
Now we install and configure Nginx as a reverse proxy for Gitea. First, install the Nginx with the following command below:
sudo apt install nginx
Next, create an Nginx virtual host configuration:
nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/gitea.conf
Add the following file:
server {
listen 80;
server_name gitea.your-domain.com;
access_log /var/log/nginx/gitea_access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/gitea_error.log;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3000;
}
}
Save and close, then reload the restart Nginx with the following command below:
sudo systemctl restart nginx sudo systemctl enable nginx
Next, you will need to edit the Gitea app.ini file and define your domain information:
nano /etc/gitea/app.ini
Changes the following line:
DOMAIN = gitea.your-domain.com ROOT_URL = http://gitea.your-domain.com/
Step 8. Accessing Gitea Web Interface.
Once successfully installed, open a web browser and visit http://gitea.your-domain.com. You should see the following page:
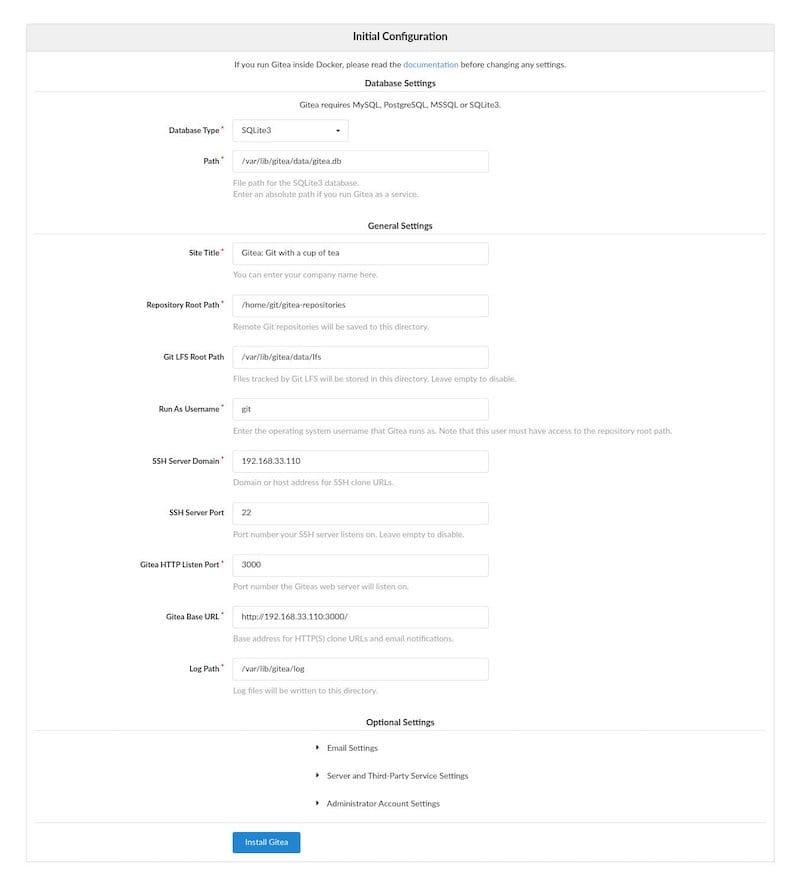
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Gitea. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the latest version of the Gitea Framework on Debian 11 Bullseye. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Gitea website.