How To Install Midnight Commander on Debian 12

Midnight Commander stands as one of the most powerful and versatile file managers available for Linux systems. This text-based dual-pane file manager provides an intuitive interface for navigating directories, managing files, and performing system operations with remarkable efficiency. For Debian 12 users, Midnight Commander represents an essential tool that combines visual clarity with command-line power. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about installing and configuring this invaluable utility on your Debian 12 system, ensuring you can harness its full potential for streamlined file management.
Understanding Midnight Commander
Midnight Commander, commonly abbreviated as MC, is a feature-rich visual file manager that operates within a text-based environment. Developed as free software, this utility draws inspiration from Norton Commander, offering a dual-pane interface that dramatically simplifies file operations. Unlike graphical file managers that rely heavily on mouse interactions, Midnight Commander emphasizes keyboard shortcuts for rapid navigation and command execution.
The strength of Midnight Commander lies in its versatility. The application provides powerful file management capabilities across local and remote systems, built-in text editing, file viewing, and directory comparison tools. For system administrators and power users working with Debian 12, these features are particularly valuable when managing server environments or performing complex file operations.
What makes Midnight Commander especially appealing is its ability to function efficiently even in environments with limited resources or over SSH connections. The application’s text-based interface ensures consistent performance across various terminal types and connection methods, making it an ideal choice for both desktop environments and remote server management scenarios.
Prerequisites for Installation
Before proceeding with the installation of Midnight Commander on your Debian 12 system, several prerequisites should be addressed to ensure a smooth installation process.
System Requirements:
- A working Debian 12 installation (either desktop or server edition)
- Administrative privileges (sudo access) for installation
- Terminal access to your system
- Active internet connection for downloading packages
Verify System Readiness:
To begin, ensure your system is up-to-date by opening a terminal and updating the package index:
sudo apt updateThis command refreshes your system’s knowledge of available packages from the configured repositories. Having sudo privileges is essential for the installation process, as it requires system-wide modifications.
Additionally, confirm that your network connection is functioning properly. A simple ping test can verify this:
ping -c 4 google.comIf your connection is working, you’ll receive responses from the server. With these prerequisites satisfied, you’re ready to proceed with preparing your system for Midnight Commander installation.
Preparing Your Debian System
Before installing Midnight Commander, it’s crucial to properly prepare your Debian 12 system. This preparation ensures that the installation proceeds smoothly and that you have access to the necessary package repositories.
Update Package Repositories:
First, refresh your system’s package index to ensure you have the most current information about available packages:
sudo apt updateVerify Repository Configuration:
Midnight Commander is available in Debian’s main repositories, but it’s important to verify that your system is correctly configured to access these repositories. Check your sources list file:
cat /etc/apt/sources.listEnsure that your sources.list file contains entries for the main Debian repositories. A properly configured file should include lines similar to:
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian bookworm main
deb http://security.debian.org/debian-security bookworm-security main
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian bookworm-updates mainIf these lines are missing or commented out (preceded by a # character), you’ll need to edit the file to enable them.
Fix Repository Issues:
If you encounter repository issues, you can edit the sources.list file:
sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.listUncomment (remove the # from) any lines referencing the main repositories, then save the file and exit the editor. After making changes, update your package index again:
sudo apt updateWith your system properly prepared, you’re now ready to proceed with installing Midnight Commander using one of several available methods.
Method 1: Installing MC via APT Package Manager
The simplest and most recommended approach for installing Midnight Commander on Debian 12 is using the Advanced Package Tool (APT), Debian’s native package management system. This method ensures proper integration with your system and handles dependencies automatically.
Step 1: Update Package Index
Begin by ensuring your package index is current:
sudo apt updateThis command refreshes the list of available packages and their versions, ensuring you install the latest version of Midnight Commander.
Step 2: Install Midnight Commander
With your package index updated, install Midnight Commander with a single command:
sudo apt install mcThe system will display the packages to be installed, including any dependencies required by Midnight Commander. You’ll see output similar to:
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
The following additional packages will be installed:
mc-data
Suggested packages:
arj catdvi djvulibre-bin gv imagemagick odt2txt poppler-utils
python python-boto python-tz xpdf | pdf-viewer
The following NEW packages will be installed:
mc mc-data
0 upgraded, 2 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded.
Need to get 2,145 kB of archives.
After this operation, 7,856 kB of additional disk space will be used.
Do you want to continue? [Y/n]Press Y and Enter to confirm the installation.
Step 3: Verify Installation
After the installation completes, verify that Midnight Commander installed correctly by checking its version:
mc --versionThis command should display the installed version of Midnight Commander, confirming a successful installation.
The APT installation method offers several significant advantages:
- Simplicity and speed of installation
- Automatic dependency resolution
- Integration with Debian’s package management system
- Easy updates through standard system update procedures
For most Debian 12 users, this installation method provides the ideal balance of convenience and functionality, making it the recommended approach for adding Midnight Commander to your system.
Method 2: Installing Midnight Commander from Source
While the APT package manager provides a convenient installation method, installing from source code gives you greater control over the build process and allows access to the latest features. This method is ideal for users who need specific customization options or want the very newest version of Midnight Commander.
Step 1: Install Build Dependencies
First, install the packages needed to compile Midnight Commander:
sudo apt install build-essential libglib2.0-dev libslang2-dev libssh2-1-dev libx11-dev gettext libgpm-devStep 2: Download the Source Code
Navigate to a directory where you want to download the source code:
cd /tmpDownload the latest stable version of Midnight Commander from the official website:
wget https://ftp.osuosl.org/pub/midnightcommander/mc-4.8.28.tar.xzNote that the version number may be different by the time you read this article.
Step 3: Extract the Source Code
Extract the downloaded archive:
tar -xvf mc-4.8.28.tar.xzStep 4: Configure the Build
Navigate to the extracted directory and run the configuration script:
cd mc-4.8.28
./configure --prefix=/usrThe --prefix=/usr option specifies that Midnight Commander should be installed in the /usr directory, making it available system-wide.
Step 5: Compile the Source Code
Compile Midnight Commander with the following command:
makeThis process may take several minutes depending on your system’s performance.
Step 6: Install the Compiled Program
Once compilation completes, install Midnight Commander:
sudo make installStep 7: Verify the Installation
Confirm that Midnight Commander installed correctly:
mc --versionInstalling from source offers several advantages:
- Access to the latest features and bug fixes
- Ability to customize build options
- Fine-grained control over installation parameters
- Opportunity to modify the source code if needed
However, this method requires more technical knowledge and time investment compared to APT installation. For most users, the APT method will be sufficient, but building from source remains valuable for those requiring specific customizations or features not yet available in the repository version.
Method 3: Alternative Installation Methods
Beyond the standard APT installation and source compilation, Debian 12 users have access to alternative package management systems for installing Midnight Commander. These methods provide different advantages depending on your specific needs and workflow.
Using Flatpak
Flatpak offers a containerized approach to application installation, providing consistent behavior across different Linux distributions.
Step 1: Install Flatpak Support
Begin by installing Flatpak on your Debian system:
sudo apt install flatpakStep 2: Add the Flathub Repository
Add the Flathub repository, which hosts numerous Flatpak applications:
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoStep 3: Install Midnight Commander
Install Midnight Commander using Flatpak:
flatpak install flathub org.midnightcommander.mcStep 4: Launch Flatpak Version
Launch the Flatpak version of Midnight Commander:
flatpak run org.midnightcommander.mcUsing Snap
Snap packages are another universal packaging system that works across many Linux distributions.
Step 1: Install Snap Support
Install Snap on your Debian system:
sudo apt install snapdStep 2: Install Midnight Commander
Install Midnight Commander using Snap:
sudo snap install mcStep 3: Launch Snap Version
Launch the Snap version by simply typing:
mcEach alternative installation method offers distinct benefits:
- Flatpak: Provides isolation from the host system and consistent behavior across distributions
- Snap: Offers automatic updates and simplified installation of complex applications
For most Debian 12 users, the standard APT installation remains the most straightforward approach. However, these alternative methods provide valuable options for specific use cases, particularly when working across multiple distributions or requiring more isolated application environments.
Configuring Midnight Commander
After successfully installing Midnight Commander, configuring it to match your preferences can significantly enhance your productivity. The application offers extensive customization options through both its interface and configuration files.
Configuration Files Location:
Midnight Commander stores its configuration in several locations:
- System-wide settings:
/etc/mc/ - User-specific settings:
~/.config/mc/
The primary configuration file is ini, located in your user’s configuration directory.
Basic Configuration Through Interface:
Launch Midnight Commander and press F9 to access the main menu. Navigate to “Options” to configure various aspects of the application:
- Panel Options: Customize how file panels display information
- Configuration: Modify core behavior settings
- Layout: Adjust the visual arrangement of interface elements
- Display Bits: Configure character encoding options
Color Scheme Configuration:
To modify the color scheme, navigate to “Options” > “Appearance” from the main menu. Here you can select from predefined color schemes or create your own.
For more advanced customization, you can edit the color skin files in ~/.config/mc/skins/.
Keyboard Shortcuts Configuration:
Midnight Commander’s keyboard shortcuts can be customized to match your workflow:
- Press F9 to access the main menu
- Select “Configuration” > “Edit key bindings”
- Navigate to the action you wish to modify
- Press the desired key combination to assign it
Panel Display Options:
Configure how file listings appear in the panels:
- Press F9 to access the main menu
- Select “Options” > “Panel options”
- Choose between “Brief listing format,” “Long listing format,” or “Custom listing format”
These configuration options allow you to tailor Midnight Commander to your specific needs, creating a file management environment that aligns perfectly with your workflow and preferences.
Basic Usage Tutorial
Once Midnight Commander is installed and configured, learning its basic operations will help you navigate and manage files efficiently. The dual-pane interface provides an intuitive environment for file operations while offering powerful keyboard shortcuts for rapid task execution.
Launching Midnight Commander:
To start the application, simply open a terminal and type:
mc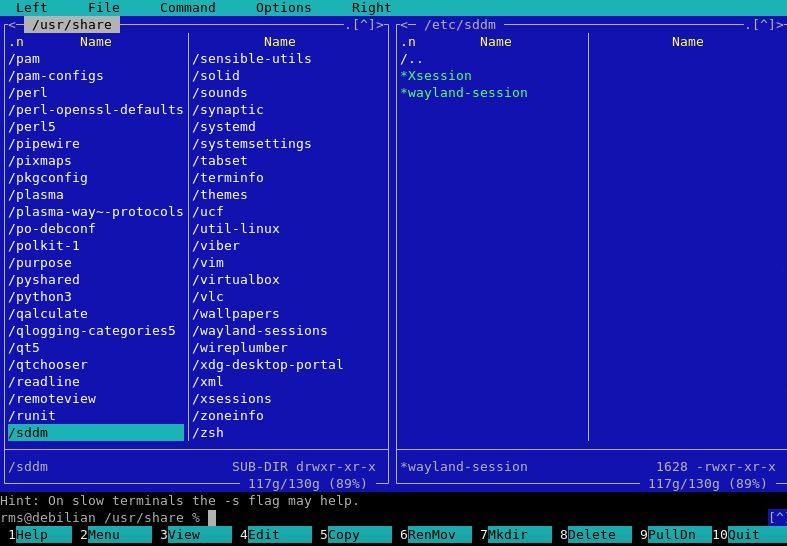
Understanding the Interface:
When Midnight Commander launches, you’ll see:
- Two file panels showing directory contents
- Function key shortcuts at the bottom of the screen
- Command line area below the panels
- Menu bar accessible via F9
Basic Navigation:
- Use arrow keys to move between files and directories
- Press Tab to switch between left and right panels
- Press Enter to open directories or files
- Use the “..” entry to navigate up one directory level
- Press Alt+s to search for files
File Operations:
- F5: Copy selected files/directories
- F6: Move or rename files/directories
- F7: Create a new directory
- F8: Delete selected files/directories
- F3: View file contents
- F4: Edit file (using internal editor)
Selection Operations:
- Insert: Select a file or directory
- + (plus): Select files by pattern
- \ (backslash): Unselect files by pattern
- * (asterisk): Reverse selection
Using Mouse Support:
Midnight Commander supports mouse operations in most terminal emulators:
- Click on files to select them
- Double-click to open files or directories
- Click on function key labels to execute their actions
- Scroll wheel to navigate through listings
Command Execution:
To execute shell commands while in Midnight Commander:
- Simply type the command in the command line area at the bottom
- Press Enter to execute
- The output appears in the terminal, and pressing any key returns to MC
Menu Navigation:
Press F9 to access the top menu bar, then use arrow keys to navigate between options. Press Enter to select a menu item or Esc to cancel.
This basic usage knowledge provides a foundation for working with Midnight Commander. As you become more comfortable with these operations, you’ll discover additional features that can further enhance your file management productivity on Debian 12.
Advanced Features
Midnight Commander offers a wealth of advanced features that extend far beyond basic file management. These capabilities transform it from a simple file manager into a comprehensive system administration and development tool.
Built-in Editor (mcedit):
Midnight Commander includes a powerful text editor accessible by pressing F4 on a file. The editor features:
- Syntax highlighting for numerous programming languages
- Block operations (select, copy, move, delete)
- Search and replace with regular expression support
- Macro recording and playback
- Multiple file editing with tabs
To access the editor directly from the command line:
mcedit filenameFile Viewer (mcview):
Press F3 to view file contents with advanced features:
- Support for binary and text files
- Hex mode for examining binary data
- Search functionality
- Wrapped or unwrapped text display
To launch the viewer directly:
mcview filenameWorking with Archives:
MC can browse and manipulate archive files as if they were directories:
- Navigate into archives by pressing Enter
- Add, extract, or delete files within archives
- Supported formats include ZIP, TAR, GZ, BZ2, and many others
FTP/SFTP Connections:
Access remote servers directly within the interface:
- Press F9 to access the menu
- Select “Left” or “Right” > “SFTP link”
- Enter connection details like
sftp://username@server.example.com
This feature allows seamless management of files across local and remote systems.
Shell Integration:
MC integrates with the shell in several ways:
- Press Ctrl+O to toggle between MC and the underlying shell
- Use the subshell feature to maintain directory context between MC and shell
- Execute commands with selected filenames by pressing Ctrl+Enter
Bookmarks and Hotlist:
Create shortcuts to frequently accessed locations:
- Navigate to the desired directory
- Press Ctrl+\ to open the hotlist
- Select “Add current” to bookmark the location
- Name your bookmark for easy reference
Directory Comparison:
Compare and synchronize directories:
- Navigate to the source directory in one panel
- Navigate to the target directory in the other panel
- Press F9 and select “Commands” > “Compare directories”
- MC highlights files that differ between directories
These advanced features demonstrate Midnight Commander’s extraordinary versatility, making it an indispensable tool for system administrators and power users working with Debian 12 systems.
Troubleshooting Common Installation Issues
Even with straightforward installation procedures, users occasionally encounter issues when installing Midnight Commander on Debian 12. Understanding common problems and their solutions can save significant time and frustration.
Package Not Found Errors:
If you receive a “package not found” error when attempting to install Midnight Commander, the most likely cause is improperly configured repositories.
Solution:
- Check your sources list:
cat /etc/apt/sources.list - Ensure the main repositories are enabled (not commented out with #)
- Add missing repositories if necessary:
sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.listAdd or uncomment the following lines:
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian bookworm main deb http://security.debian.org/debian-security bookworm-security main - Update your package index:
sudo apt update - Try installing again:
sudo apt install mc
Dependency Resolution Problems:
Sometimes installation fails due to unresolved dependencies.
Solution:
- Fix potential package issues:
sudo apt --fix-broken install - Ensure your system is up-to-date:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade - Try reinstalling with automatic dependency resolution:
sudo apt install -f mc
Permission Errors:
Installation may fail if you lack sufficient permissions.
Solution:
- Ensure you’re using sudo for installation commands
- Check that your user account has sudo privileges:
groupsYour username should appear in the sudo group
Display and Terminal Compatibility Issues:
After installation, Midnight Commander may display incorrectly in some terminals.
Solution:
- Set the correct terminal type:
export TERM=xterm-256color - Launch MC with specific terminal settings:
TERM=xterm-256color mc - For SSH sessions with display issues, try:
mc -dThis disables mouse support and may resolve some display glitches.
Source Compilation Errors:
When installing from source, compilation may fail due to missing development packages.
Solution:
- Install a comprehensive set of build dependencies:
sudo apt install build-essential libglib2.0-dev libslang2-dev libgpm-dev libssh2-1-dev libx11-dev gettext - Clear previous build attempts before trying again:
make clean ./configure make
By addressing these common issues, most installation problems can be resolved quickly, allowing you to proceed with using Midnight Commander on your Debian 12 system.
Customizing Midnight Commander
Tailoring Midnight Commander to your specific preferences can significantly enhance productivity and user experience. Beyond basic configuration, several customization options allow you to transform MC’s appearance and behavior to match your workflow perfectly.
Installing Custom Skins:
Midnight Commander supports custom skins that change its entire appearance:
- Download or create a skin file (with .ini extension)
- Place it in
~/.config/mc/skins/directory - Select the skin through Options > Appearance
- Popular skins include darkfar, gotar, and modarcon16
To activate a skin directly through the command line:
mc -S skinnameFor example, to use the “dark” skin:
mc -S darkCreating Custom Menus:
Extend Midnight Commander’s functionality with custom menu entries:
- Edit the user menu file:
mcedit ~/.config/mc/menu - Add custom commands in the format:
+ "Menu Entry Name" command %f - Use placeholders like %f (current file) or %d (current directory)
- Example for compressing the selected file:
+ "Compress to .tar.gz" tar -czvf %f.tar.gz %f
Configuring Panel Layout:
Customize how information appears in file panels:
- Press F9 and select Options > Layout
- Toggle options like “Menubar visible,” “Command prompt,” or “Keybar visible”
- Configure “Horizontal split” or “Vertical split” for panels
- Adjust panel sizes by dragging the divider with your mouse
Setting Up Extension-Specific Actions:
Configure MC to handle specific file types with dedicated applications:
- Edit the extension file:
mcedit ~/.config/mc/mc.ext - Add rules for file extensions:
# PDF files regex/i/\.pdf$ Open=evince %f & View=evince %f &
This example opens PDF files with Evince when you press Enter or F3.
These customization options demonstrate Midnight Commander’s flexibility, allowing you to create a tailored file management environment that perfectly aligns with your specific needs and preferences on Debian 12.
Updating and Maintaining MC
Proper maintenance ensures your Midnight Commander installation remains secure, stable, and equipped with the latest features. Following best practices for updates and maintenance will extend the utility’s lifespan and functionality on your Debian 12 system.
Checking for Updates:
When installed via APT, Midnight Commander receives updates through Debian’s standard update mechanism:
sudo apt update
sudo apt list --upgradable | grep mcIf an update is available, upgrade with:
sudo apt upgrade mcFor source installations, check the official website or repository for new versions and follow the source installation steps with the new version.
Configuration Backup:
Before making significant changes or updates, back up your Midnight Commander configuration:
cp -r ~/.config/mc ~/mc-config-backupThis creates a backup of your user-specific configuration, which can be restored if needed:
rm -rf ~/.config/mc
cp -r ~/mc-config-backup ~/.config/mcClean Removal:
If you need to completely remove Midnight Commander, use the appropriate command based on your installation method:
For APT installations:
sudo apt remove mcTo remove configuration files as well:
sudo apt purge mcFor source installations:
cd /path/to/mc/source
sudo make uninstallFor Flatpak installations:
flatpak uninstall org.midnightcommander.mcFor Snap installations:
sudo snap remove mcBest Practices for Maintenance:
- Keep your entire Debian system updated regularly
- Check for MC updates when updating other system packages
- Periodically review and clean up custom configurations
- Test new versions in a non-critical environment before updating production systems
- Subscribe to security announcements for potential vulnerabilities
By following these maintenance guidelines, you’ll ensure your Midnight Commander installation remains an effective and reliable tool for file management on your Debian 12 system.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Midnight Commander. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Midnight Commander on Debian 12 “Bookworm” system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Midnight Commander website.