How To Install Monit on Fedora 36

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Monit on Fedora 36. For those of you who didn’t know, Monit is an open-source utility for monitoring and managing Unix systems. Monit monitors the server programs to increase service uptime and ensures that they stay online consistently. With Monit, system status can be viewed directly from the command line, or via the native HTTP web server.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the Monit monitoring tool on a Fedora 36.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Fedora 36.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- An active internet connection.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Monit on Fedora 36
Step 1. Before proceeding, update your Fedora operating system to make sure all existing packages are up to date. Use this command to update the server packages:
sudo dnf upgrade sudo dnf update sudo dnf install dnf-plugins-core
Step 2. Installing Monit on Fedora 36.
By default, the Monit package comes in the default repository of Fedora 36. Now run the following command below to install the latest version of Monit to your Fedora 36 system:
sudo dnf install monit
Once is done, start the service of the Monit and then enable the same, so that it could start itself automatically with the system reboot:
sudo systemctl enable monit sudo systemctl start monit
Step 3. Configure Monit.
Monit is very easy to configure, in fact, the configuration files are created to be very easily readable and make them easier for users to understand. The main configuration file of monit located at /etc/monit:
nano /etc/monit.conf
Modify the following configuration:
set httpd port 2812 and
use address 0.0.0.0 # only accept connections from localhost
allow 0.0.0.0/0 # allow localhost to connect to the server and
allow admin:monit # require user 'admin' with password 'monit'
allow @monit # allow users of group 'monit' to connect (rw)
allow @users readonly # allow users of group 'users' to connect readonly
Save and close the file, then restart Monit service to take the effect of the change:
sudo systemctl restart monit
Step 4. Configure Firewall.
Now we configure the firewall to allow access to the Monit web interface, running on port 2812:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=2812/tcp sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Step 5. Accessing Monit Web Interface.
Once successfully installed, open your web browser and access Monit using the URL http://your-IP-address:2821. You will see the following page:
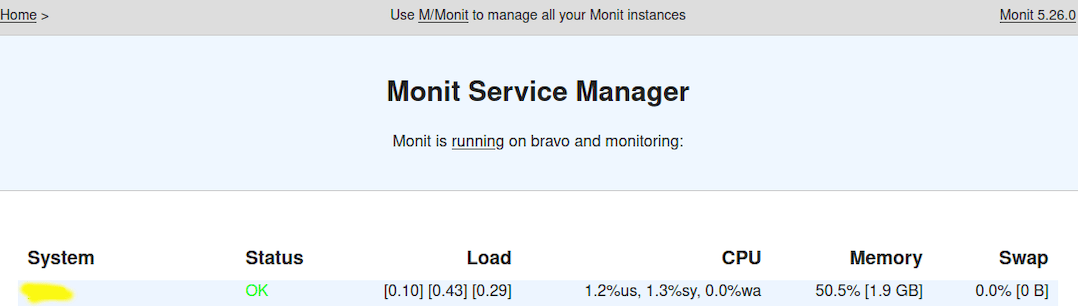
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Monit. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Monit monitoring tool on your Fedora 36 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Monit website.