How To Install Prometheus on openSUSE

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Prometheus on openSUSE. Prometheus is an open-source monitoring system and time-series database. It provides a multi-dimensional data model, a flexible query language, and autonomous server nodes with no reliance on distributed storage.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the Prometheus monitoring tool on openSUSE.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: openSUSE.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- You will need access to the terminal to execute commands. openSUSE provides the Terminal application for this purpose. It can be found in your Applications menu.
- You’ll need an active internet connection to download Prometheus and its dependencies.
- You’ll need administrative (root) access or a user account with sudo privileges.
Install Prometheus on openSUSE
Step 1. The first step in any installation process is to ensure your system is up-to-date. On openSUSE Linux, this can be achieved using the zypper package manager. Open your terminal and type the following command:
sudo zypper refresh sudo zypper update
Step 2. Installing Prometheus on openSUSE.
Next, download the Prometheus binary from the official website. You can use the curl command to download the file:
wget https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus/releases/download/v2.49.1/prometheus-2.49.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
After downloading, extract the file and rename the extracted folder to prometheus-files:
tar -xvf prometheus-2.49.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz mv prometheus-2.49.1.linux-amd64 prometheus-files
Then, move the Prometheus files to the /etc/prometheus directory and change the ownership to the prometheus user:
sudo cp -r prometheus-files/consoles /etc/prometheus sudo cp -r prometheus-files/console_libraries /etc/prometheus sudo chown -R prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheus
Step 3. Configuring Prometheus.
Create and configure the prometheus.yml file:
sudo nano /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
Add the following content to the prometheus.yml file:
global:
scrape_interval: 10s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'prometheus'
scrape_interval: 5s
static_configs:
- targets: ['localhost:9090']
Change the ownership of the file to the prometheus user:
sudo chown prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
Step 4. Setting Up Prometheus as a Service.
Create a Prometheus service file:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/prometheus.service
Add the following content to the file:
[Unit]
Description=Prometheus
Wants=network-online.target
After=network-online.target
[Service]
User=prometheus
Group=prometheus
Type=simple
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/prometheus \
--config.file /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml \
--storage.tsdb.path /var/lib/prometheus/ \
--web.console.templates=/etc/prometheus/consoles \
--web.console.libraries=/etc/prometheus/console_libraries
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Reload the systemd manager configuration:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
Start the Prometheus service and enable it to start at boot:
sudo systemctl start prometheus sudo systemctl enable prometheus
Step 5. Installing and Configuring Node Exporter.
Node Exporter is a Prometheus exporter for hardware and OS metrics with pluggable metric collectors. It allows you to measure various machine resources such as memory, disk I/O, CPU, network, etc.
First, download and set up Node Exporter:
wget https://github.com/prometheus/node_exporter/releases/download/v1.7.0/node_exporter-1.7.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz tar -xvf node_exporter-1.7.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz mv node_exporter-1.7.0.linux-amd64 node_exporter-files
Copy the Node Exporter binary to /usr/bin and change the ownership to the node_exporter user:
sudo cp node_exporter-files/node_exporter /usr/bin/ sudo chown node_exporter:node_exporter /usr/bin/node_exporter
Create a Node Exporter service file:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/node_exporter.service
Add the following configuration:
[Unit] Description=Node Exporter After=network.target [Service] User=node_exporter ExecStart=/usr/bin/node_exporter [Install] WantedBy=default.target
Reload the systemd manager configuration, start the Node Exporter service, and enable it to start at boot:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl start node_exporter sudo systemctl enable node_exporter
Step 6. Configuring Firewall Rules.
If your firewall is enabled and running, add rules to allow access to Prometheus and Node Exporter ports:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=9090/tcp sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=9100/tcp sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Step 7. Accessing Prometheus Web UI.
Once successfully installed, open a web browser and navigate to http://<your_server_ip>:9090. You should see the Prometheus dashboard.
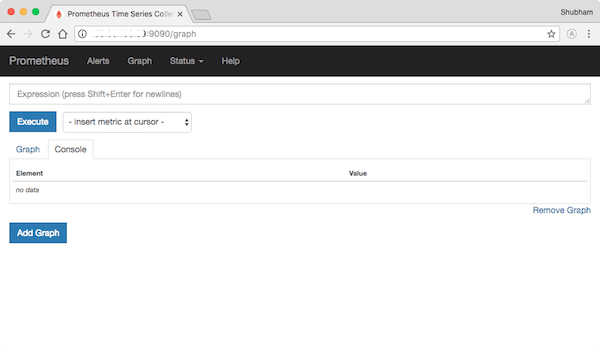
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Prometheus. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Prometheus open-source monitoring tool on your openSUSE system. For additional or useful information, we recommend you check the official Prometheus website.