
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install and configure Django on Debian 9 Stretch. For those of you who didn’t know, Django is the most popular Python web framework designed to help developers build secure, scalable, and maintainable web applications. Django is free and open-source software.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of Django on a Debian 9 (Stretch) server.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Debian 9 (Stretch).
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Django on Debian 9 Stretch
Step 1. Before we install any software, it’s important to make sure your system is up to date by running the following apt-get commands in the terminal:
apt-get update apt-get upgrade
Step 2. Installing PIP and necessary dependencies.
Now you can install pip using the following command:
sudo apt install python3-venv
Step 3. Creating a Virtual Environment.
Create a new directory for your Django application and navigate into it:
mkdir my_django_app cd my_django_app
Next, execute the following command to create a new virtual environment:
python3 -m venv venv
To start using the virtual environment, activate it by running the activate script:
source venv/bin/activate
Step 4. Installing Django on Debian 9.
Once the pip is installed, run the following command to install Django:
pip install django
You can test that the installation was successful by typing:
python -m django --version
Step 5. Create a sample Django project.
Now that the Django framework has been installed, you can give it a test drive by creating a sample project:
cd ~ django-admin startproject myproject
The command above will create a directory myproject in your working directory ~, and store all necessary files within.
Run the commands below in sequence to get your application started. Follow the instructions on the screen to provide the superuser’s credentials:
cd myproject/ python3 manage.py migrate python3 manage.py createsuperuser python3 manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000
Step 6. Accessing Django.
Django will be available on HTTP port 8080 by default. Open your favorite browser and navigate to http://your-domain.com:8000 or http://server-ip:8000/admin
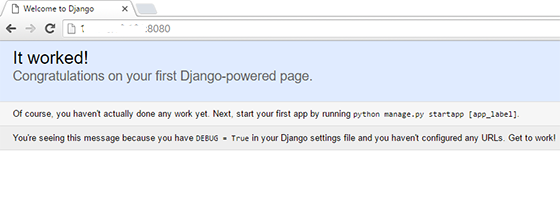
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Django. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Django web framework on Debian 9 Stretch server. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Django website.